HTTP node
An HTTP node lets you make HTTP requests to external APIs or services directly from your flow. Use it to integrate with third-party systems, fetch data from REST APIs, or send data to webhooks and external endpoints. The output of the HTTP request becomes available to subsequent nodes in your flow.
Configure the HTTP request
Selecting an HTTP node opens a side panel with two tabs: Parameters and Test.
Parameters
Configure the following settings on the Parameters tab:
-
URL (required): The endpoint URL for the HTTP request. You can insert dynamic values from previous nodes using the + button.
-
Method (required): The HTTP method to use. Supported methods include
GET,POST,PUT,PATCH, andDELETE.
Query params
Add query parameters to append to the request URL. Select Add new query param to define key-value pairs that are automatically appended to the URL as query string parameters.
Headers
Add custom HTTP headers to the request. Select Add new header to define key-value pairs such as Authorization, Content-Type, or any custom headers required by the target API.
Body
Enter the request body content for methods that support it (e.g., POST, PUT, PATCH). You can insert dynamic values from previous nodes using the + button.
If a chip is in brackets, it will render as an array of values. Otherwise, it will render as a single value for each request.
Pagination
Enable Use pagination to automatically handle paginated API responses. This is useful when an API returns results across multiple pages and you need to retrieve all of them in a single flow execution.
HTTP client config
Fine-tune the behavior of the HTTP client:
-
Timeout (seconds): The maximum time to wait for a response before the request times out. Default is
30seconds. -
Max retries: The number of times to retry a failed request. Default is
3. -
Follow redirects: When enabled, the HTTP client automatically follows redirect responses (e.g.,
301,302). Enabled by default.
Test the HTTP request
Use the Test tab to send a test request to the API using the defined parameters. A successful request populates the test output tab with the response data, allowing you to validate the configuration before publishing your flow.
Example: Fetch carbon intensity for an AWS region
This example shows how to use an HTTP node to fetch the current carbon intensity for the us-east-1 AWS region using the Electricity Maps API. This can be useful in a FinOps flow that monitors or compares carbon emissions across regions to support sustainability goals.
To follow this example, create a free API key on the Electricity Maps platform.
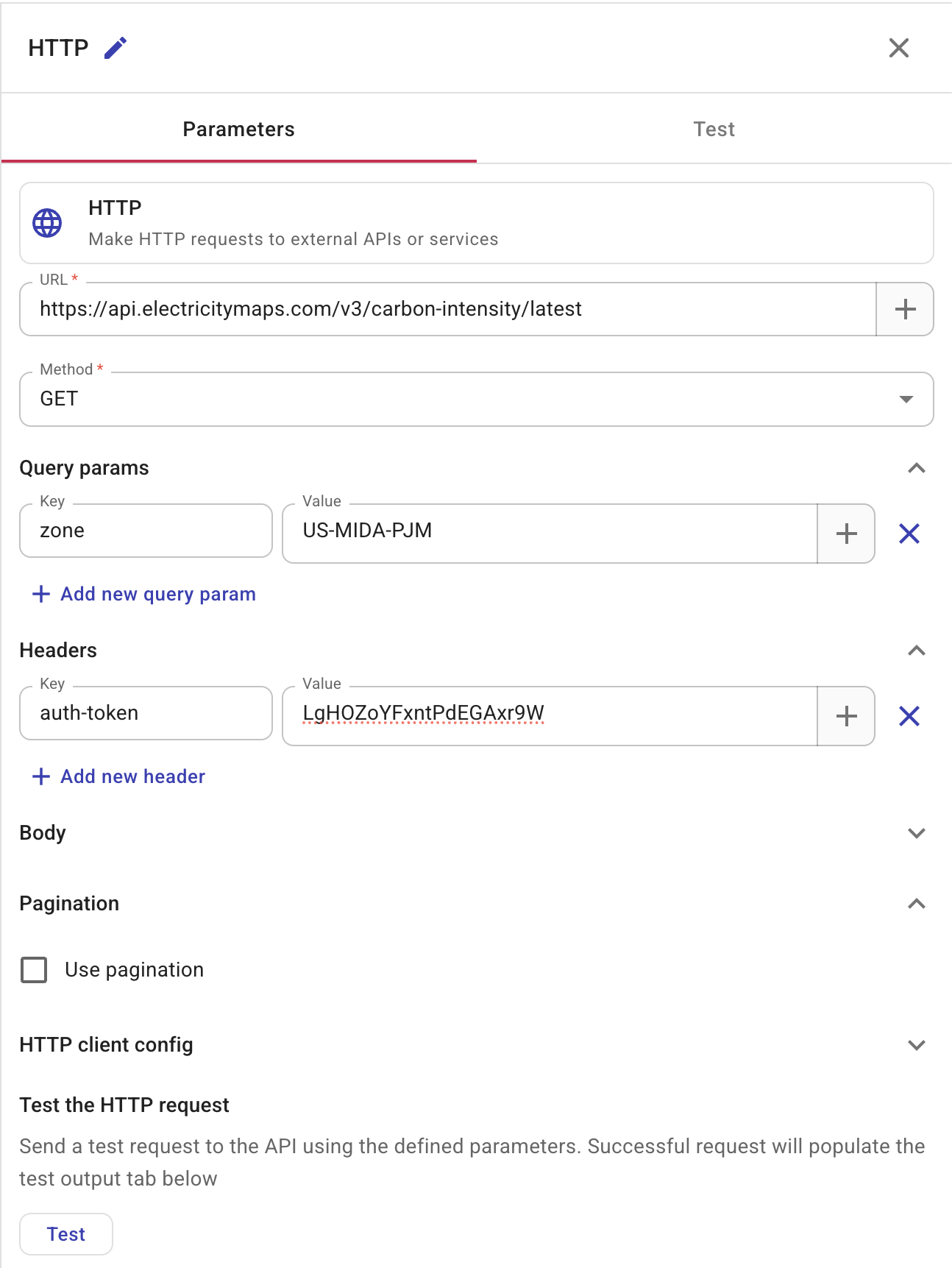
Configure the HTTP node with the following settings:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | https://api.electricitymaps.com/v3/carbon-intensity/latest |
| Method | GET |
| Query params | zone = US-MIDA-PJM |
| Headers | auth-token = your Electricity Maps API key |
The US-MIDA-PJM zone corresponds to the PJM grid, which covers the us-east-1 AWS region.
Select Test to send the request. A successful response returns the current carbon intensity for the zone:
{
"zone": "US-MIDA-PJM",
"carbonIntensity": 406,
"datetime": "2026-02-15T20:00:00.000Z",
"updatedAt": "2026-02-15T19:25:13.450Z",
"createdAt": "2026-02-15T08:39:54.714Z",
"emissionFactorType": "lifecycle",
"isEstimated": true,
"estimationMethod": "SANDBOX_MODE_DATA"
}
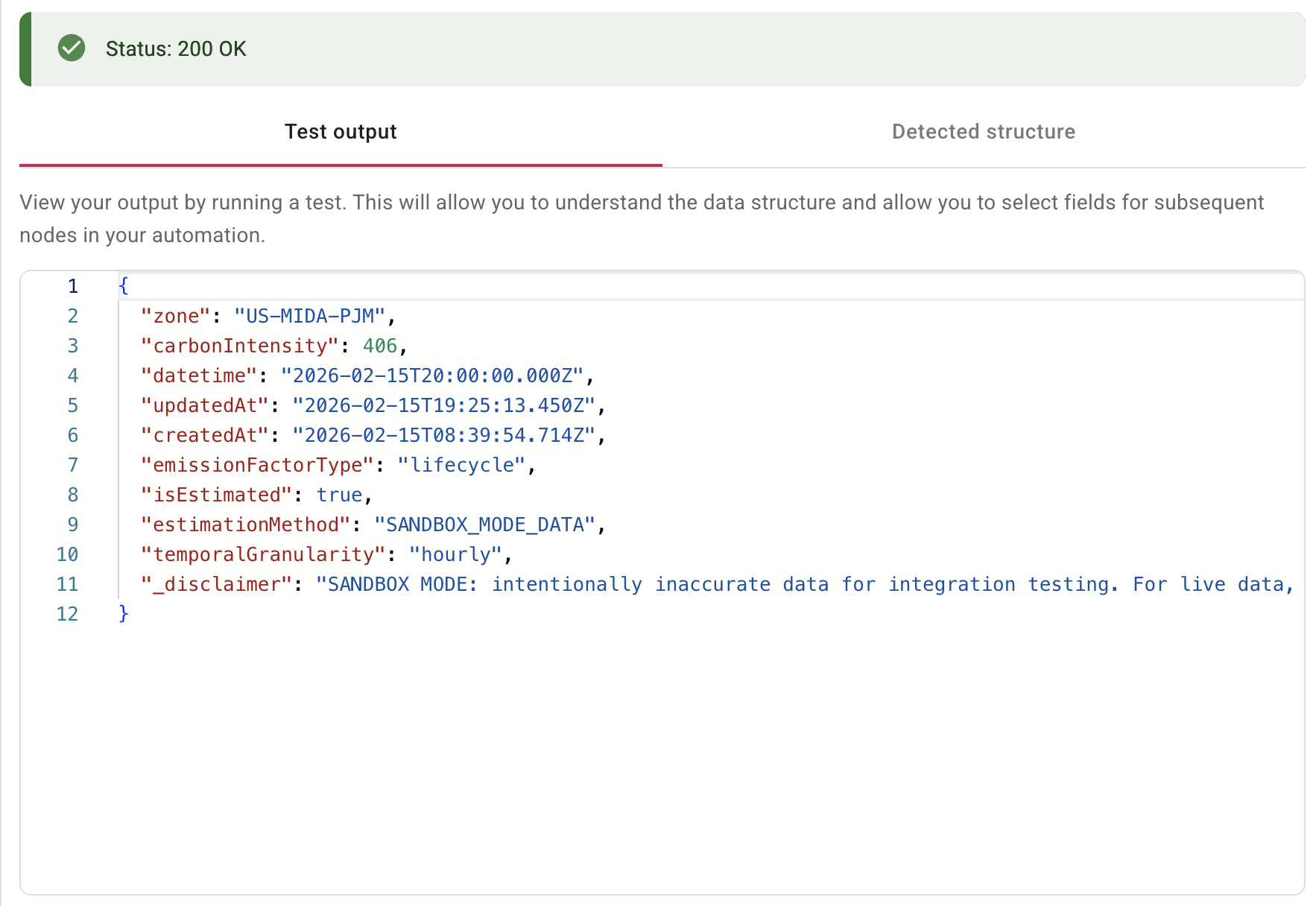
You can then use this data in subsequent nodes — for example, a Branch node to check if carbonIntensity exceeds a threshold, and a Notification node to alert stakeholders when emissions are high.