AWS real-time anomaly detection
Supported services
DoiT supports near real-time anomaly detection for the following AWS services:
-
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
-
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS). For provisioned RDS instances, the following components are supported:
-
DB Instance hours: Based on the type of DB instance consumed.
-
Storage (per GB per month): Based on the storage capacity you have provisioned to your DB instance.
-
Provisioned IOPS per month: Provisioned IOPS rate, regardless of IOPS consumed (For Amazon RDS Provisioned IOPS storage only).
-
AWS CloudTrail
To activate AWS real-time anomaly detection, you need to have AWS CloudTrail in place and enable the real-time anomaly feature on the relevant AWS accounts.
We recommend creating a multi-Region trail to log events in all AWS Regions. If you have created an organization in AWS Organizations, you can create a multi-Region organization trail to log events in all regions of all AWS accounts in that organization.
S3 bucket's region
When creating the trail, you must choose an Amazon S3 bucket created in one of the following regions to store the CloudTrail log files:
-
us-east-1,us-east-2,us-west-2 -
eu-west-1,eu-central-1,eu-west-2,eu-west-3 -
ap-northeast-1,ap-southeast-1,ap-southeast-2 -
ca-central-1
S3 event notification
When enabling real-time anomaly on an AWS account, you need to configure an Amazon S3 event notification (event type s3:ObjectCreated:*) for the CloudTrail bucket, targeting the real-time anomaly SNS topic.
-
If you create the IAM role automatically, DoiT will configure the S3 bucket's notifications to target the real-time anomaly SNS topic.
-
If you create the IAM role manually, you must add the notification configuration via the Amazon S3 console or the AWS CloudShell (CLI).
AWS supports only a single destination for each event notification type. Ensure that the CloudTrail S3 bucket does not already have the s3:ObjectCreated:* event type configured for another destination.
S3 access
The real-time anomaly detection feature requires access solely to your CloudTrail S3 bucket.
To adhere to the Principle of least privilege, when creating the IAM role for DoiT, use "arn:aws:s3:::${CloudTrailBucketName}/*" in the IAM policy to limit access to the specified CloudTrail S3 bucket. See Feature permissions: IAM policies for Real-time anomalies for an example.
Enable real-time anomaly on AWS accounts
You can enable real-time anomaly detection when linking a new account or editing an existing one. Real-time anomaly detection should be enabled only for AWS accounts that host CloudTrail log files.
Enable on a new account
-
Sign in to the DoiT console, select Integrate from the top navigation bar, and then select AWS.
-
On the Link Amazon Web Services page, select Link account.
-
Provide information about the S3 bucket that stores the CloudTrail logs. Note that the configuration varies with the way you create the AWS IAM role.
-
Create a role automatically: Select the Real-time anomalies feature and enter the S3 bucket name.
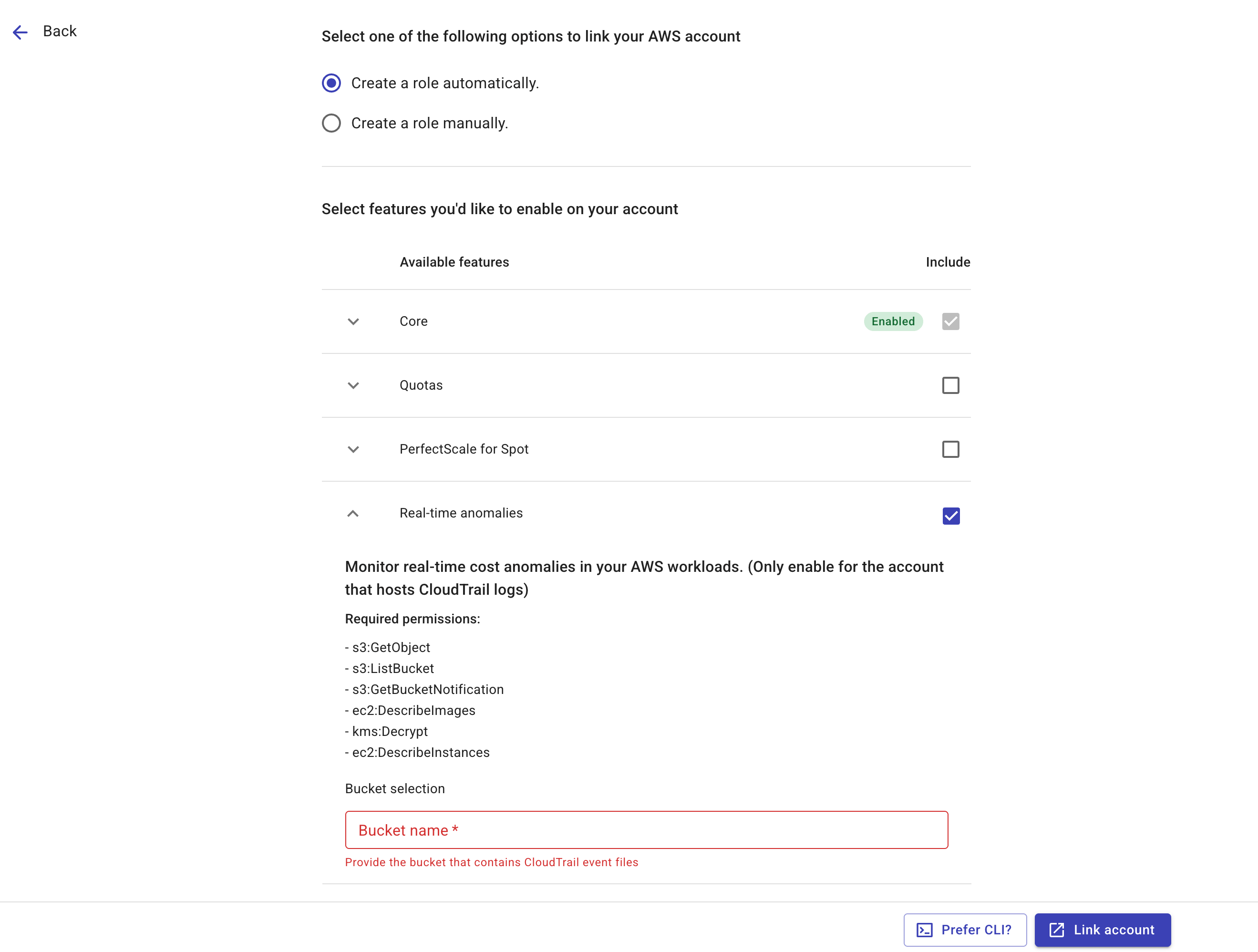 Tip
TipThe CloudFormation stack created for the IAM role also grants the
s3:GetBucketLocationands3:PutBucketNotificationpermissions, which are necessary for the DoiT Real-time anomaly feature to locate the bucket and add an AWS CloudTrail bucket notification. You can remove these two permissions after the account has been successfully linked. See Real-time anomalies for more information about the required permissions. -
Create a role manually: Enter the S3 bucket name and specify the region where the bucket resides.
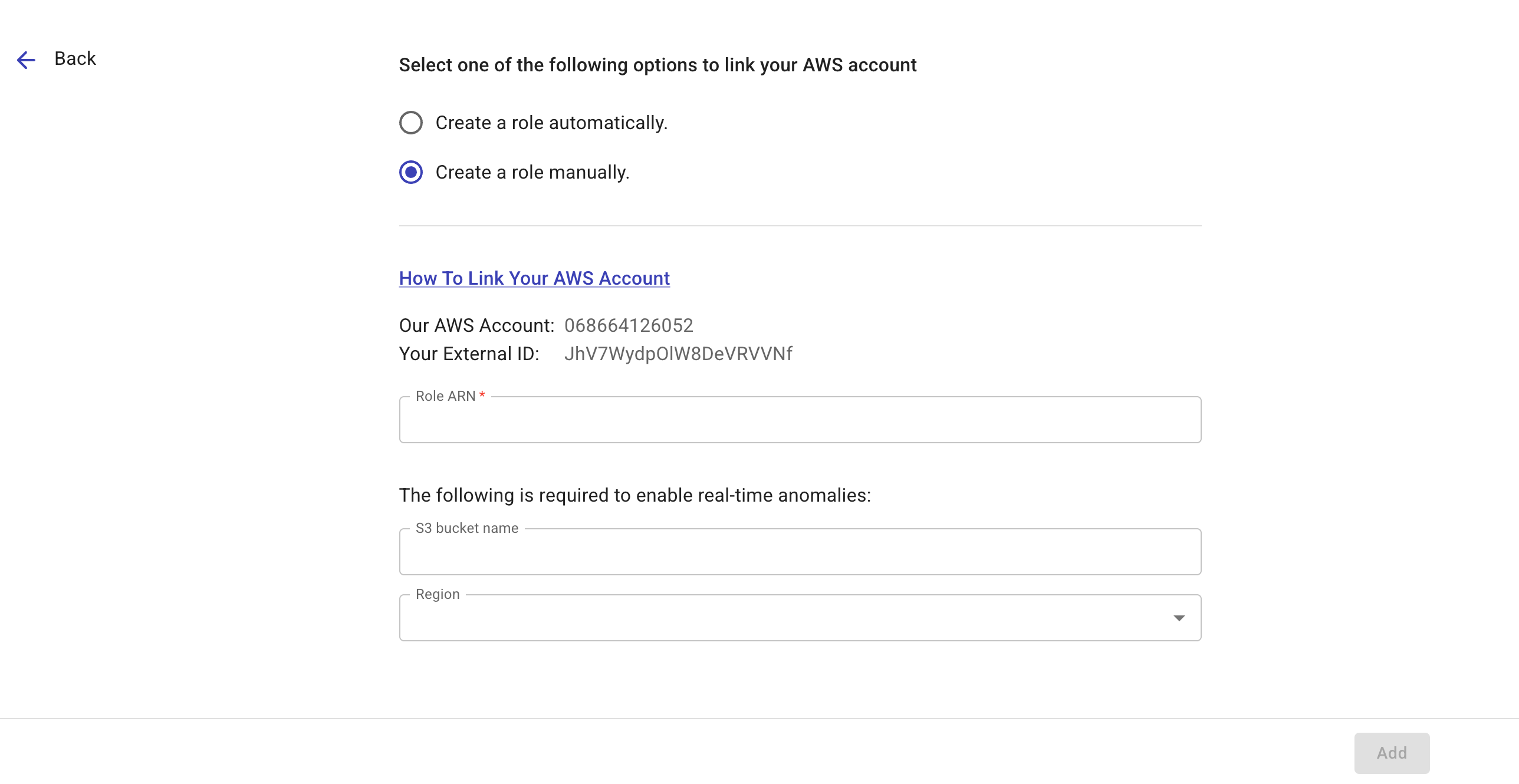
-
Configure S3 bucket event notification
If you create the IAM role manually, after linking your AWS account, you must configure an Amazon S3 event notification for the bucket to send events to the DoiT SNS topic. You can add the notification via the Amazon S3 console or the AWS CloudShell (CLI).
To add the S3 bucket notification via the AWS CLI:
-
Identify the region where your CloudTrail S3 bucket is located. The SNS topic ARN must match the region where your S3 bucket is located.
-
Run the AWS CLI command based on your bucket's region:
Replace
<S3_BUCKET_NAME>with your CloudTrail bucket name and<S3_BUCKET_REGION>with your bucket's region before running the command.- `us-east-1` region
- Any other region
If your S3 bucket is in the
us-east-1region:aws s3api put-bucket-notification-configuration --bucket <S3_BUCKET_NAME> --notification-configuration '{
"TopicConfigurations": [
{
"Id": "NotifyCrossAccountSNSTopic",
"TopicArn": "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:676206900418:realtime-event-topic-trigger",
"Events": ["s3:ObjectCreated:*"]
}
]
}'If your S3 bucket is in any other region:
aws s3api put-bucket-notification-configuration --bucket <S3_BUCKET_NAME> --notification-configuration '{
"TopicConfigurations": [
{
"Id": "NotifyCrossAccountSNSTopic",
"TopicArn": "arn:aws:sns:<S3_BUCKET_REGION>:676206900418:realtime-event-topic-trigger-<S3_BUCKET_REGION>",
"Events": ["s3:ObjectCreated:*"]
}
]
}'
Enable on an existing account
To enable real-time anomalies on an already linked account:
-
Locate the account of interest on the Link Amazon Web Services page.
-
Select the kebab menu (⋮) at the rightmost end of the account entry, and then select Edit account.
-
Select Real-time anomalies as the feature to add, expand the feature, and enter the name of the S3 bucket that contains CloudTrail log files. The bucket must reside in one of the supported regions.
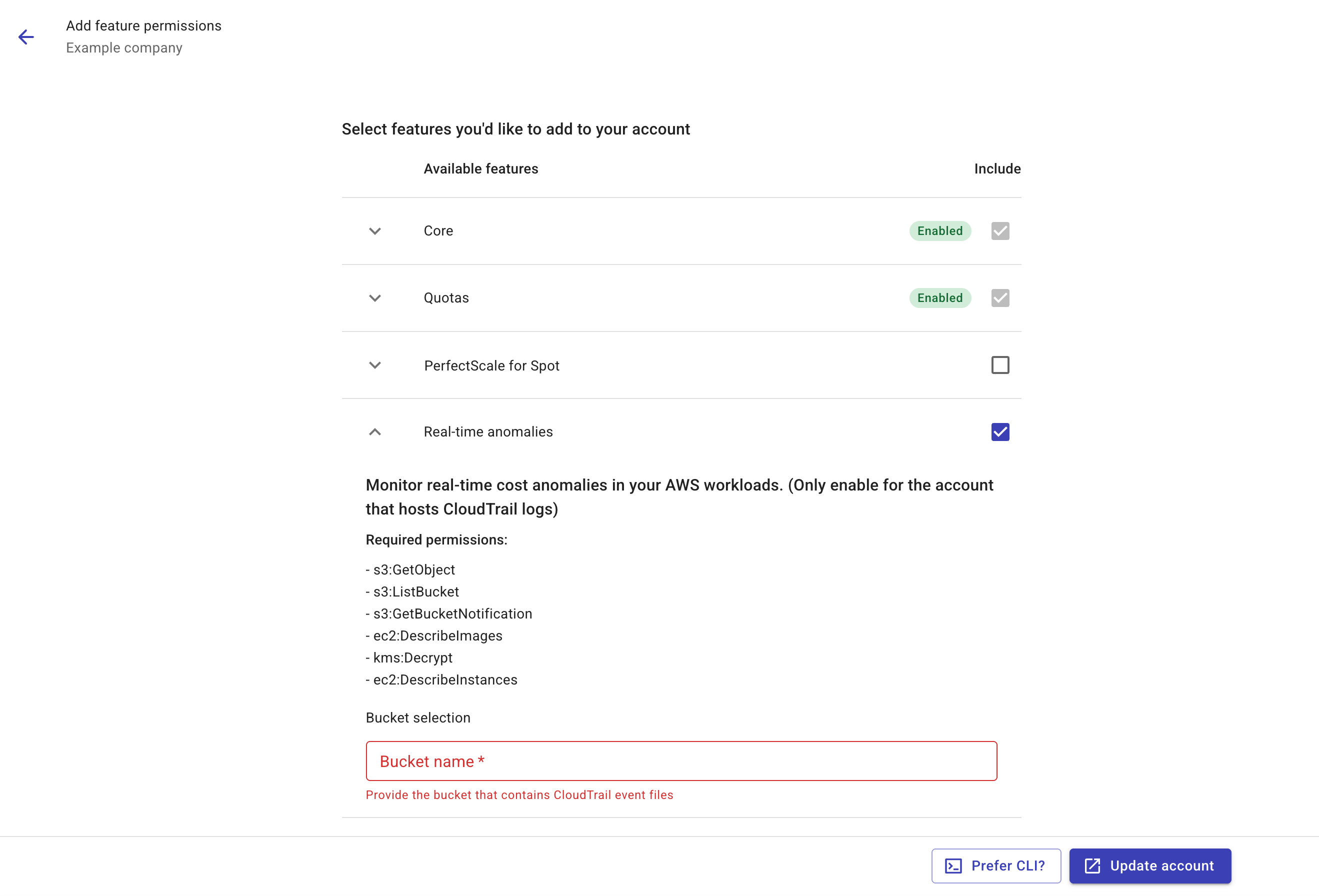
-
Select Update account to create a CloudFormation stack in the AWS console that updates the IAM role with the new permissions, or select Prefer CLI to get the command to create the CloudFormation stack via AWS CloudShell.
TipThe CloudFormation stack created for the IAM role also grants the
s3:GetBucketLocationands3:PutBucketNotificationpermissions, which are necessary for the DoiT Real-time anomaly feature to locate the bucket and add an AWS CloudTrail bucket notification. You can remove these two permissions after the account has been successfully linked. See Real-time anomalies for more information about the required permissions.
AWS multi-account environment
If your organization has an AWS multi-account environment set up with AWS Control Tower, and the KMS policy and CloudTrail S3 bucket are hosted by different accounts, to enable real-time anomaly, you need to perform two separate tasks:
-
Link the account that hosts the CloudTrail S3 bucket to the DoiT platform.
-
Grant the following permissions to the DoiT IAM role created in the previous step:
-
The permission to use the AWS KMS key that encrypts CloudTrail log files. You need to update the KMS policy to add a new statement that includes the ARN of the DoiT IAM role.
-
The
ec2:DescribeImagespermission to retrieve EC2 instance information in private images owned by the AWS account.
-
Real-time anomaly detection costs
The real-time anomaly detection feature leverages AWS CloudTrail events stored in an S3 bucket. The feature may incur costs from two aspects:
-
Management events delivered to Amazon S3: As the first copy of management events within each region is delivered free of charge, you can avoid this cost by creating a multi-Region organization trail and removing other trails that cause duplicate events recording. See AWS CloudTrail pricing and Managing CloudTrail trail costs for more information.
-
S3 Storage and access:
-
The storage cost of CloudTrail management events in S3 buckets is usually low, even for accounts with a high volume of activities.
-
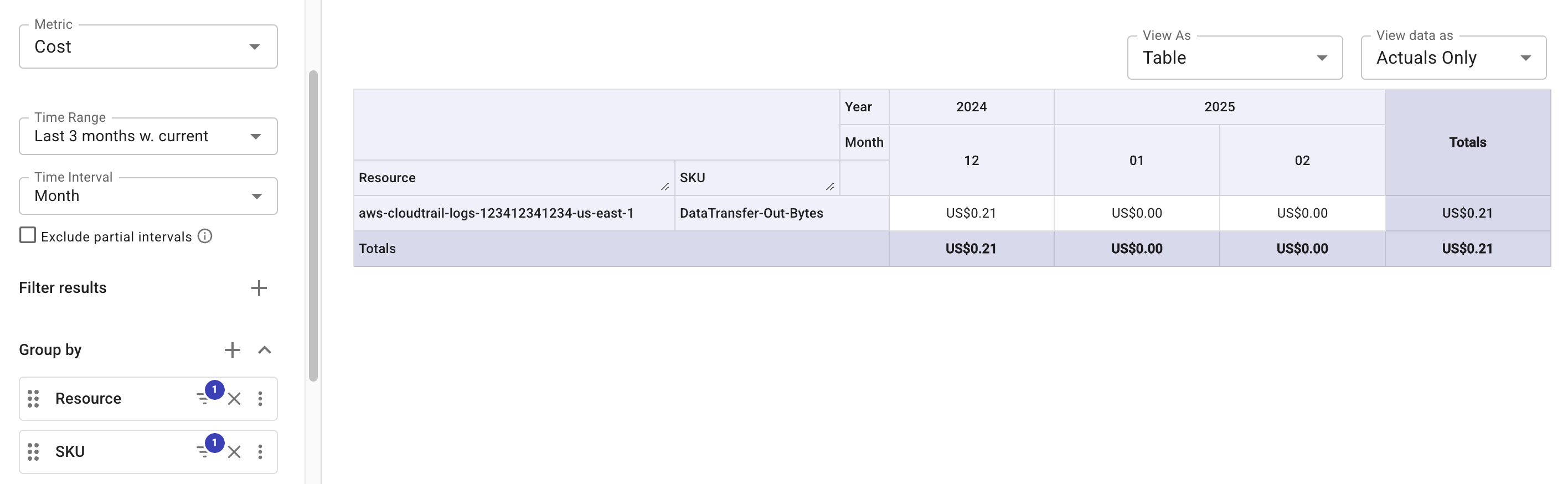
The anomaly detection engine reads the log files from the same region where the S3 bucket resides (thus avoiding the higher fee for data transferred across regions or out to the internet). The cost is charged on the SKU
DataTransfer-Out-Bytesand is usually under US$1.00 per month.
-
Below is an example report that shows the S3 costs of the real-time anomaly detection feature in recent months.
When filtering resources by S3 bucket name, if the S3 bucket you're looking for doesn't appear in the list, select the plus icon (+) to add the exact name as a new filter. See Filter results: No matches or incomplete results.