View anomaly details
When viewing the details of a specific anomaly, you have access to multiple resources that help you investigate and address the anomaly.
Required permissions
- Allocations Admin, Anomalies Viewer, Cloud Analytics User
View a cost anomaly
To view a specific cost anomaly:
-
Sign in to the DoiT console, select Monitor from the top navigation bar, and then select Cost anomalies.
-
On the Cost anomalies page, find the anomaly of interest.
-
Select View at the rightmost end of the anomaly entry to launch the cost anomaly details page.
Note that the time granularity of a cost anomaly chart varies with the data source. See below for two examples.
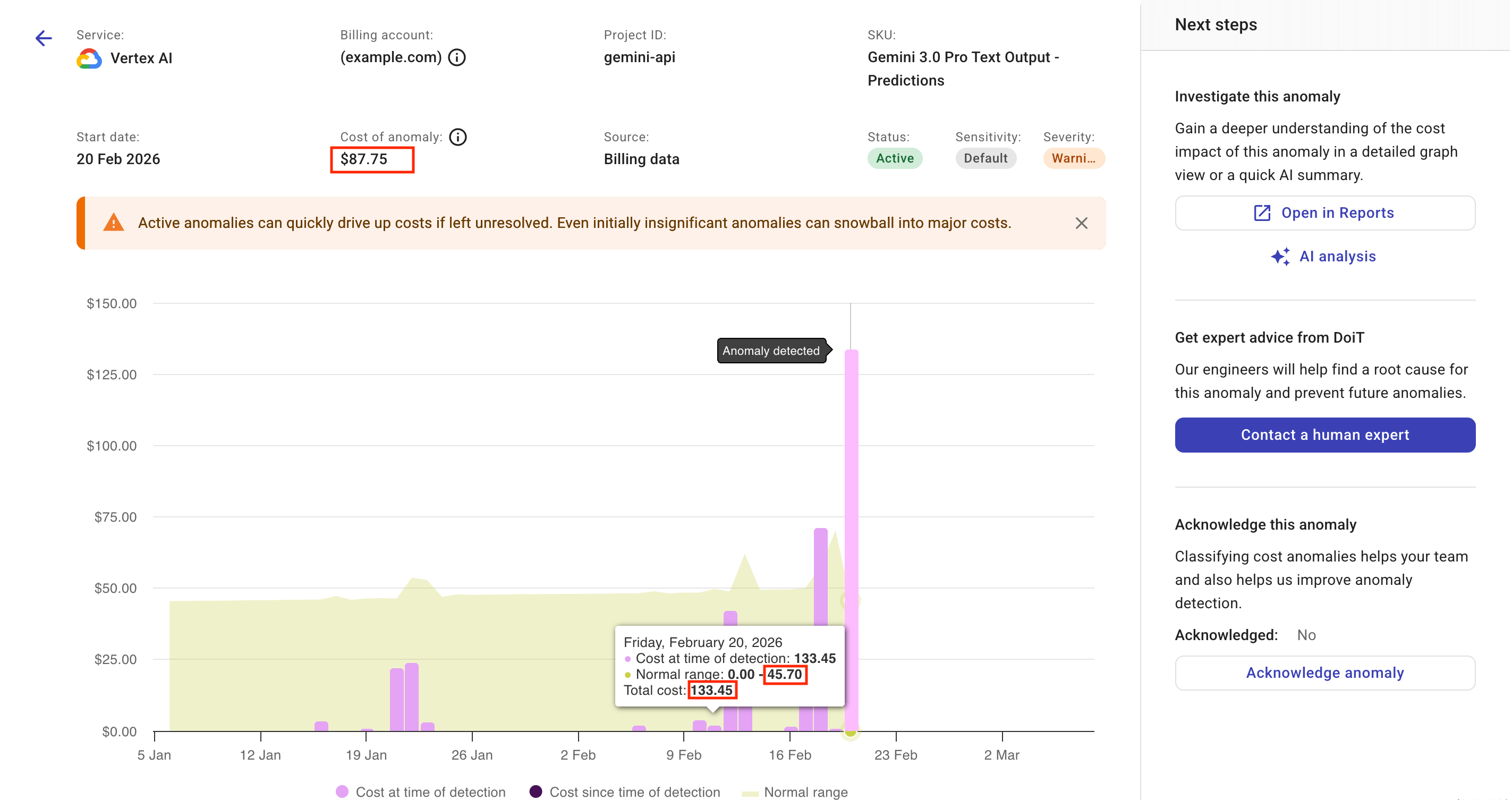
An example anomaly based on billing data (daily granularity):
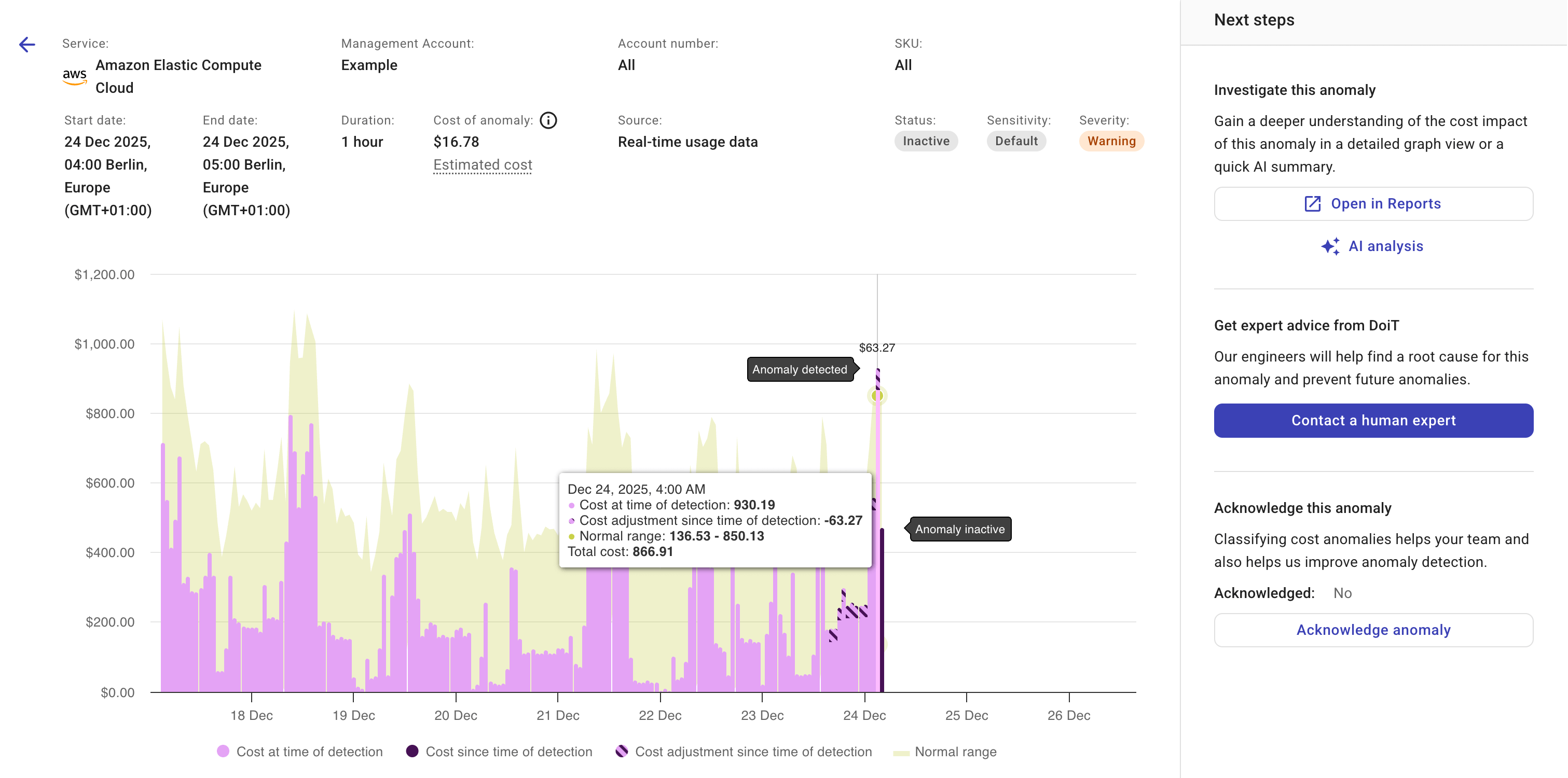
An example anomaly based on AWS CloudTrail events (Real-time anomaly, hourly granularity):
Summary
The summary information highlights the important facts about the anomaly.
In addition to anomaly properties available on the main Cost anomalies page, the summary information also includes two organizational hierarchy properties.
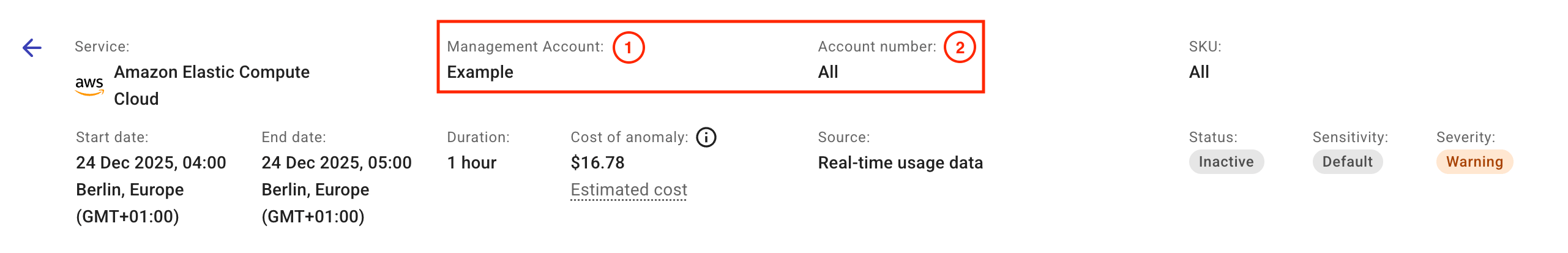
-
Apart from AWS, hierarchy property 1 maps to the Billing account dimension in the DoiT platform (see Standard dimensions).
-
Hierarchy property 2 maps to the DoiT Project/Account ID dimension. It shows All if the anomaly was detected at service level instead of at SKU level.
The table below lists the property labels for different providers or platforms:
| Provider/Platform | Hierarchy property 1 | Hierarchy property 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services | Management account/Account name (AWS account name) | Account number |
| Databricks | Organization | Account ID |
| Datadog | Account name | Workspace ID |
| Google Cloud | Billing account (Google Cloud Billing account display name and ID) | Project ID |
| Microsoft Azure | Subscription (Azure subscription display name and ID) | Resource group |
| MongoDB Atlas | Account name | Project/Account |
| OpenAI | Organization | Workspace |
| Snowflake | Organization | Account |
Cost anomaly chart
On a cost anomaly chart, you'll see two annotations indicating when a spike was identified as an anomaly (Anomaly detected) and when the anomaly became inactive (Anomaly inactive, see Dynamic updates).
Moving your mouse over the Anomaly detected bar will reveal the following numbers:
-
Cost at time of detection: Value derived from the available cost data when an anomaly was detected. This field applies only to the point of Anomaly detected.
-
Cost since time of detection: Value derived from the cost data received after an anomaly was detected. The anomaly detection system keeps updating this field until the anomaly becomes
Inactive. -
Cost adjustment since time of detection: Negative value derived from the cost data received since an anomaly was detected.
-
Normal range: It's depicted as a shaded area on an anomaly chart. The example below shows one point that exceeds the upper bound of the normal range while also meeting the other criteria. It is reported as an anomaly.
-
Cost of anomaly: The difference between the actual total cost and the maximum cost in the normal range calculated at that moment.
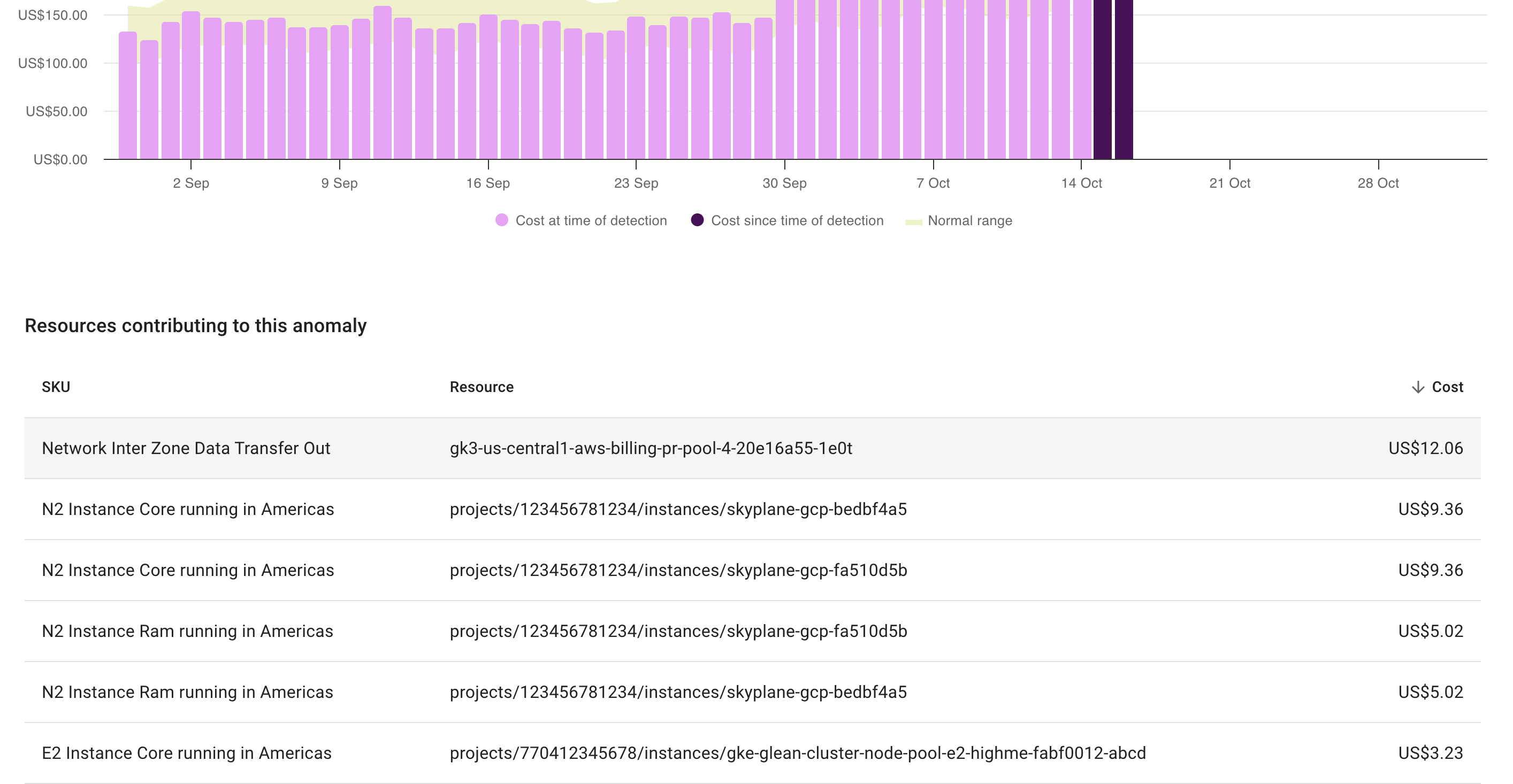
Contributory resources
A list of Resources contributing to this anomaly is displayed below the cost anomaly chart. Combining with AI analysis, this list helps you better understand what caused the anomaly and enables you to make informed decisions swiftly.
The example below shows the contributory resources of a service-level anomaly caused by multiple SKUs across different projects.
Next steps
Depending on your DoiT subscription plan and the nature of the anomaly, you can take various actions directly from the Next steps panel on the anomaly details page.
Open in reports
Cloud Analytics Reports does not support real-time usage data at this time. To investigate a real-time anomaly, try AI analysis.
To decide whether a detected anomaly is really an issue in the context of your business, select Open in Report in the upper-right corner of the cost anomaly chart. It will open a Cloud Analytics report that groups costs by SKUs and uses the provider, service, billing account, project/account ID, and allocation as filters. Select Run report to see the result.
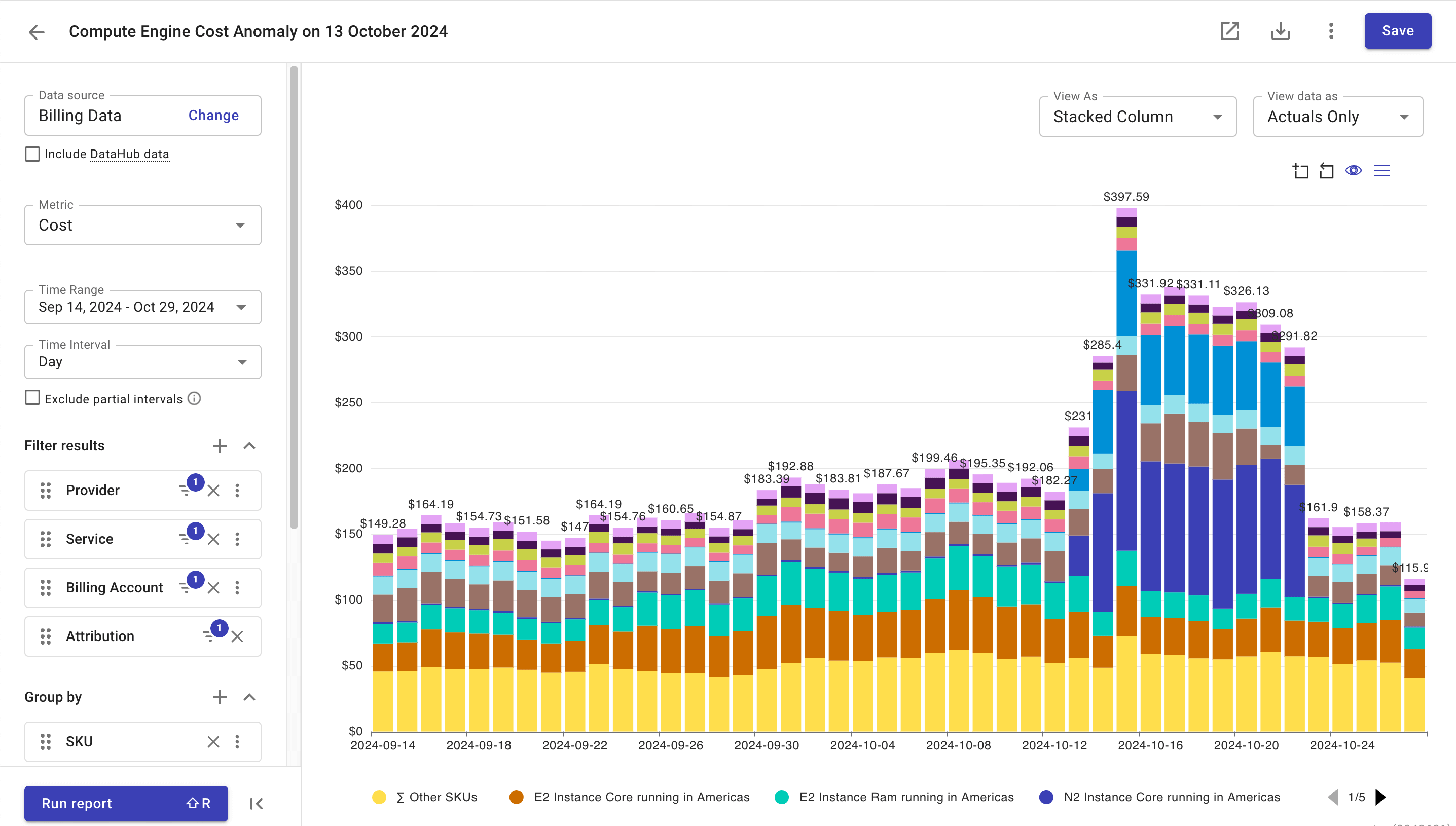
When viewing a report, be aware that reports always use the latest usage and cost data available, while the data in cost anomaly charts is only updated until the anomaly becomes Inactive.
AI analysis
When viewing an anomaly, you can select AI analysis to interact with Ava, our AI assistant.
Ava will provide an explanation of the anomaly and suggest remediation steps. It can also help you with detailed guidance on investigating the spike or fixing identified issues.
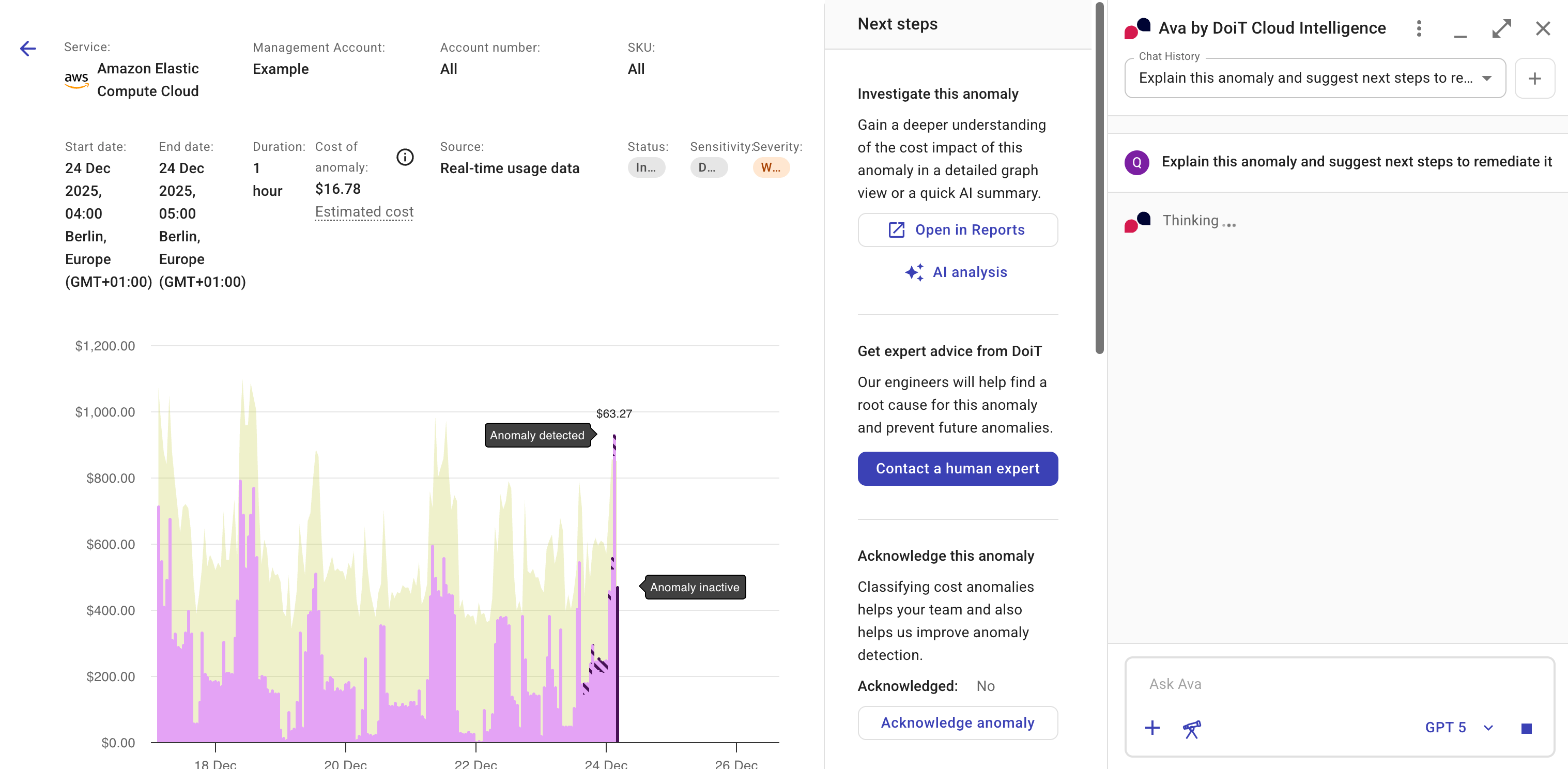
Get expert advice
If you have a DoiT Cloud Intelligence Enhanced or Enterprise plan, you can get expert advice from DoiT by selecting Contact a human expert. This will create an expert inquiry with prefilled information if applicable.
Acknowledge anomaly
An acknowledged anomaly refers to one that has been reviewed and classified. See Acknowledge anomalies.