Analyze BigQuery activities using audit data
Overview
Google Cloud generates BigQuery audit logs to record relevant administrative activities and accesses. These audit logs provide insight into operational concerns related to your BigQuery usage such as creating or deleting a table, purchasing slots, or running a load job.
The DoiT BigQuery Intelligence feature sets up a BigQuery audit log sink for widgets displayed on the BigQuery Intelligence dashboard that simplifies the analysis of BigQuery usage. You can also leverage the audit logs collected by the BigQuery Intelligence to perform your own analysis in Cloud Analytics reports, using BigQuery Intelligence as the data source.
Required permission
- Cloud Analytics User
Build reports using BigQuery Intelligence data
To build a report with data from the BigQuery Intelligence audit log sink:
-
Make sure you have already set up BigQuery Intelligence.
-
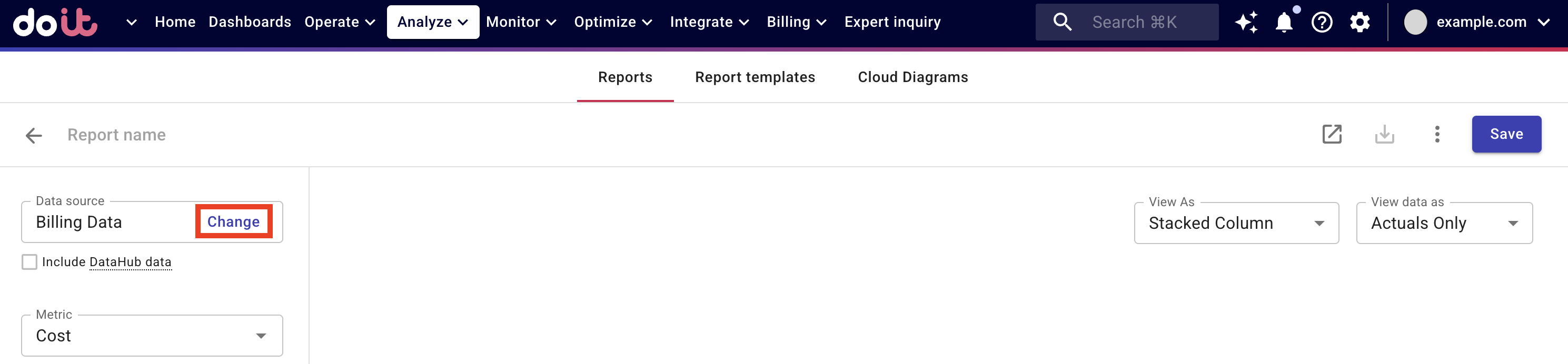
Open a report. Select Change at the top of the left-hand sidebar.
-
Select BigQuery Intelligence as the data source.
-
You can choose to Create a new report or Update the current one. Note that updating the report will lose all its current configurations.
Metrics and dimensions
Cloud Analytics reports use different sets of metrics and dimensions for billing data and BigQuery audit logs.
Metrics
The basic metrics and extended metrics for BigQuery audit logs utilize fields of the jobStatistics object in BigQuery AuditData.
Basic metrics
-
Cost: Processed bytes (
totalBilledBytes) converted to TiB multiplied by the on-demand scan price. -
Usage: Processed bytes (
totalBilledBytes) converted to TiB, adjusted by the job's CPU usage.
Extended metrics
-
Slots Used: The total number of slot-ms consumed divided by the query duration:
totalSlotMs÷ (endTime−startTime). -
Total Slots Ms: The total number of slot-ms consumed by the query job. It maps to
totalSlotMs. -
Total Load Output Bytes: Total bytes loaded for an import job. It maps to
totalLoadOutputBytes. -
Total Tables Processed: Total number of unique tables referenced in the query. It maps to
totalTablesProcessed. -
Total Billed Bytes: Processed bytes, adjusted by the job's CPU usage. It maps to
totalBilledBytes. -
Total Processed Bytes: Total bytes processed for a job. It maps to
totalProcessedBytes.
Dimensions
Below are the available standard dimensions when the report's data source is BigQuery Intelligence:
-
Event name: Name of the event. It maps to
jobCompletedEvent.eventNamein BigQuery AuditData. -
Job Status: State of a job: PENDING, RUNNING, or DONE. It maps to
jobStatus.statein BigQuery AuditData. -
Project/Account name: Human-readable Google Cloud project name of the completed job. It maps to
jobName.projectIdin BigQuery AuditData. -
Query Priority: Priority given to the query: QUERY_INTERACTIVE or QUERY_BATCH. It maps to
jobConfiguration.query.queryPriorityin BigQuery AuditData. -
Region: Location of the completed job. It maps to
jobName.locationin BigQuery AuditData. -
Reservation: Reservation name or
unreservedfor on-demand resource usage. It maps toJobStatistics.reservationin BigQuery AuditData. -
Resource: URI for the referenced resource. For example, a table created by using an insert job reports the resource URI of the table. It maps to
protoPayload.resourceNamein BigQueryAuditMetadata messages. -
Statement Type: Type of the statement. Example: SELECT, INSERT, CREATE_TABLE, CREATE_MODEL. It maps to
jobConfiguration.query.statementTypein BigQuery AuditData. -
Caller IP: IP address of the caller. It maps to
requestMetadata.callerIpin audit logs. -
User: The email address of the authenticated user (or service account on behalf of third party principal) making the request. It maps to
authenticationInfo.principalEmailin audit logs.
Examples
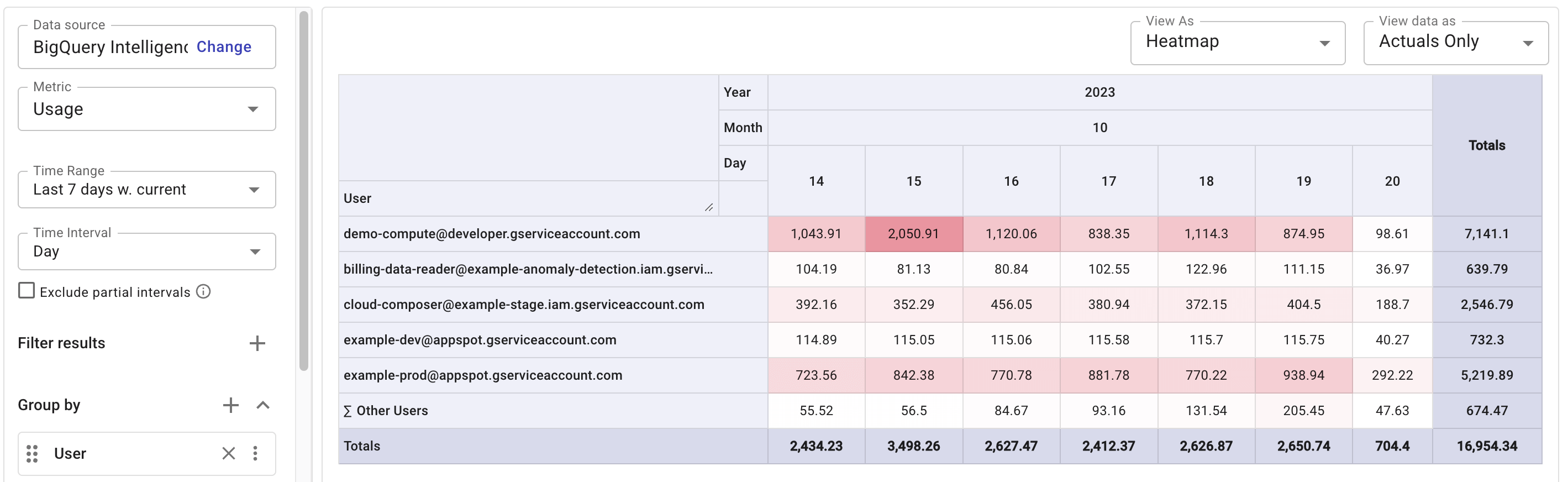
Break down usage by user
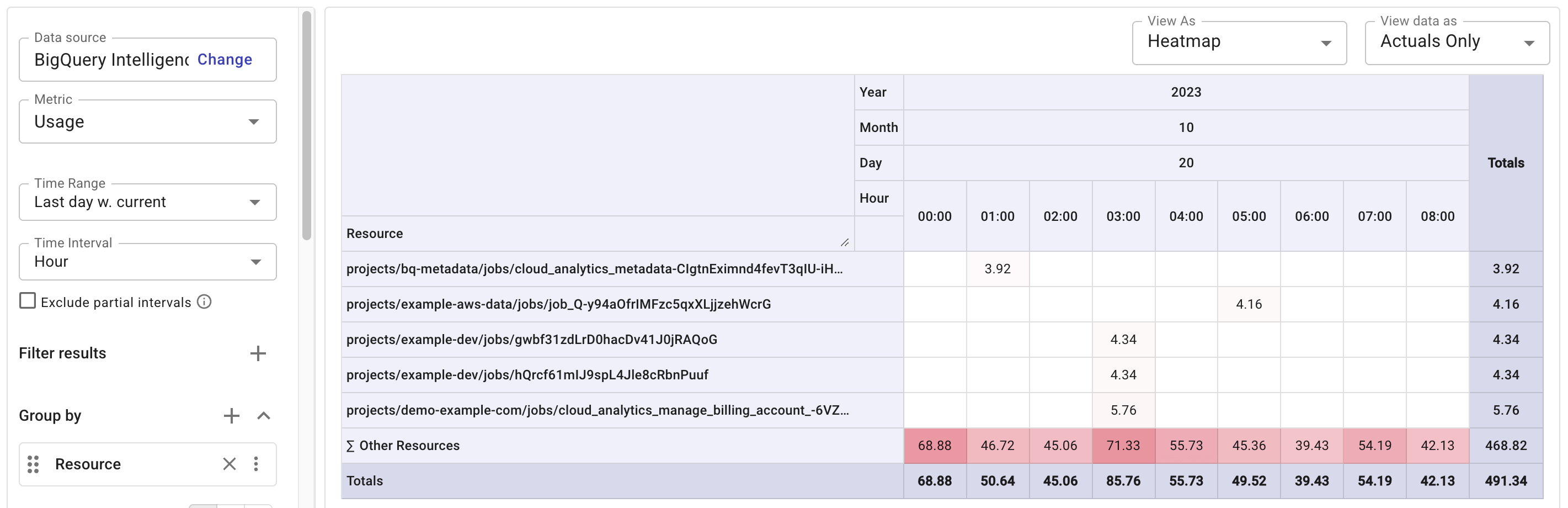
Identify hourly heavy queries by job ID
See also
-
Google Cloud Documentation: BigQuery audit logs overview
-
Google Cloud Documentation: Caller identities in audit logs