Get started
To get started with Kubernetes Intelligence, you first need to enable the Kubernetes core feature, and then onboard Kubernetes clusters.
Follow the step-by-step instructions below or check out the ▶️ interactive demo for a visual walkthrough.
Enable Kubernetes core
Enabling the Kubernetes core feature on your connected cloud accounts grants DoiT permissions to access relevant information in your environment.
- AWS account
- Google Cloud organization or project
You can enable Kubernetes core when linking a new account or editing a linked account.
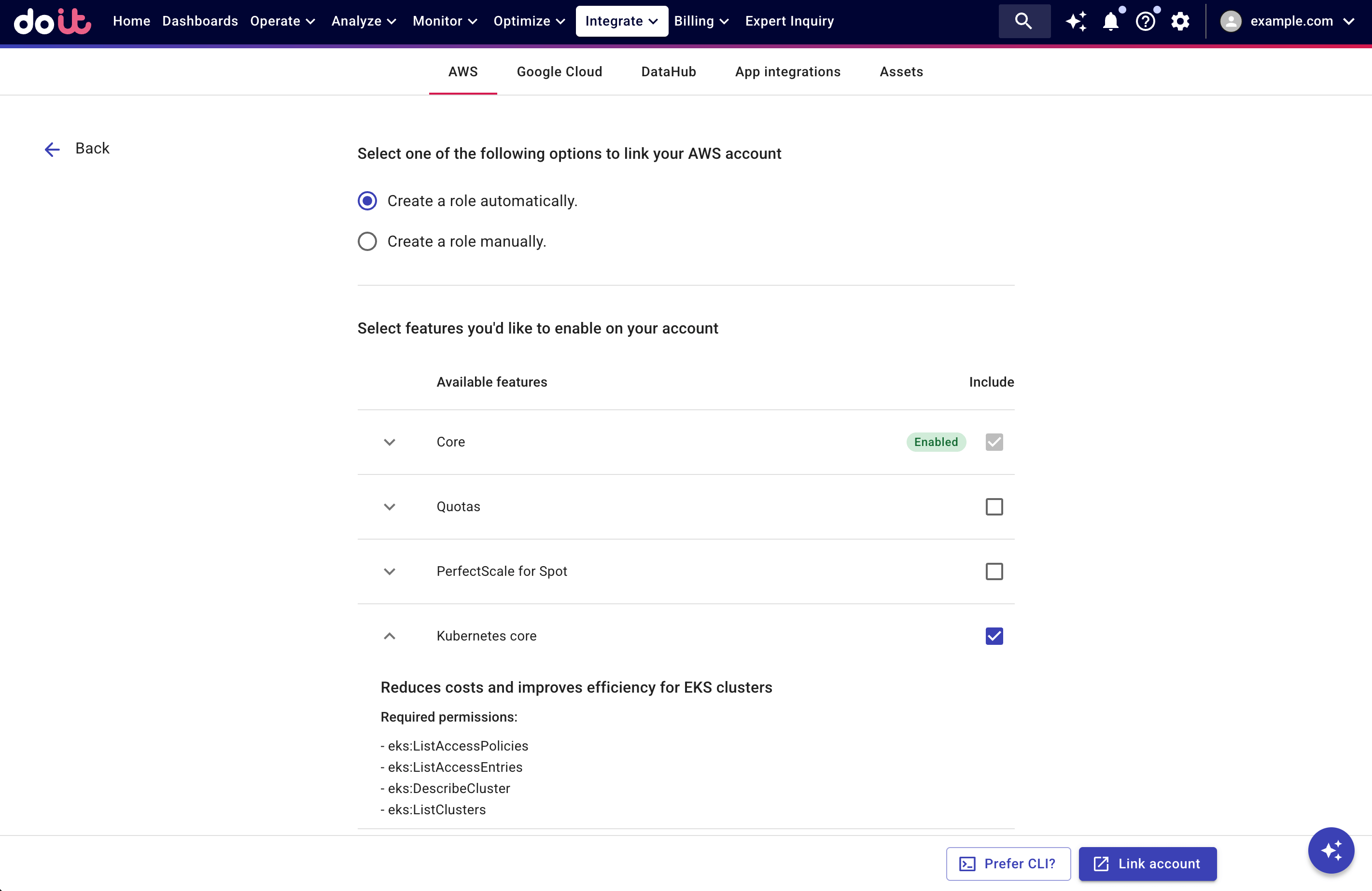
See Link your AWS account for detailed instructions; see Kubernetes core for information about the required permissions.
You can enable Kubernetes core when connecting a Google Cloud organization or project, or when editing the connection.
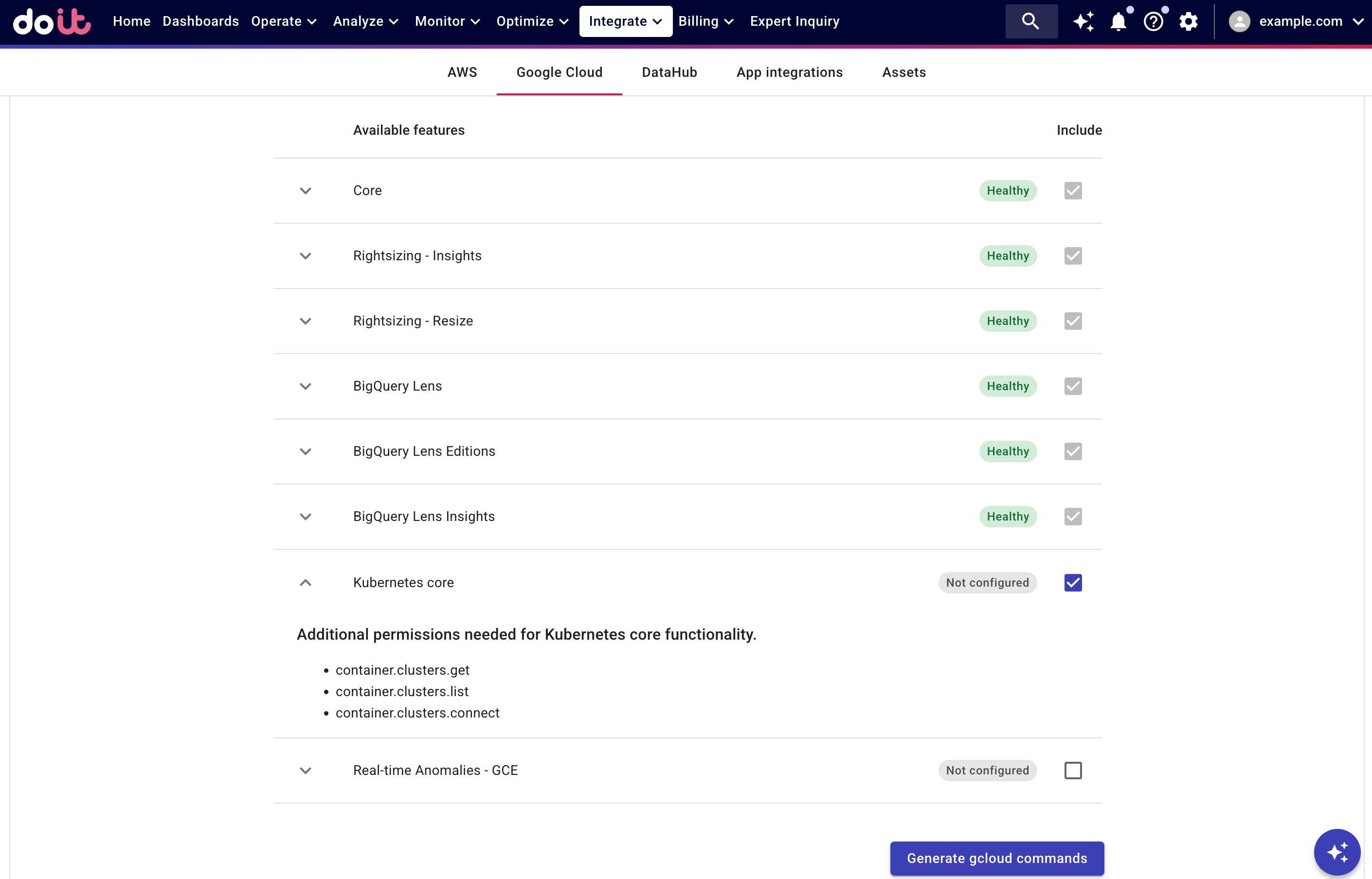
See Connect Google Cloud resources for detailed instructions; see Kubernetes core for information about the required permissions.
Once permissions are granted:
-
DoiT performs a daily scan of the connected AWS accounts and Google Cloud organizations and projects (midnight UTC for AWS, 2 AM UTC for Google Cloud) to uncover Kubernetes clusters in your cloud environment.
-
DoiT synchronizes with PerfectScale for clusters that have onboarded the PerfectScale platform.
(Optional) Connect self-managed clusters
If you have self-managed Kubernetes clusters that you want to connect to Kubernetes Intelligence (including self-managed clusters onboarded with PerfectScale), you first need to add them manually in the DoiT Console. Otherwise, skip this step and continue to Onboard clusters.
-
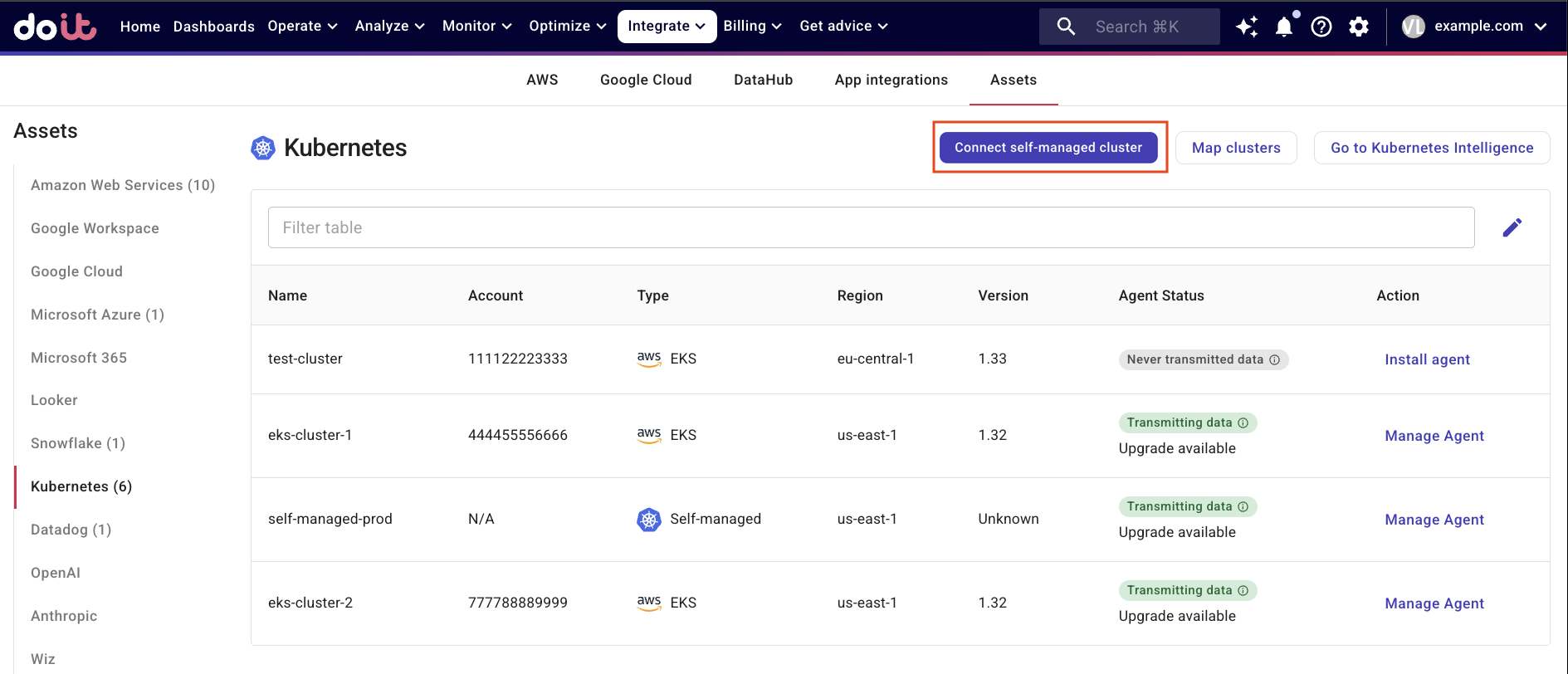
In the DoiT console, select Integrate from the top navigation bar, and then select Assets.
-
Select Kubernetes from the left-hand menu.
-
Select Connect self-managed clusters.
-
In the Add self-managed k8s cluster form, enter:
-
Name: A unique identifier for your self-managed cluster.
-
Region: (Optional) Use the Region field at your own convention, for example tag your cluster as
on-prem-cluster-1or similar. Region must be alphanumeric with hyphens, for exampleus-west-2. -
Host: The HTTPS URL endpoint of your cluster's Kubernetes API server, for example
https://k8s.example.com:6443. -
Cluster CA certificate: The Certificate Authority (CA) certificate used to verify the identity of the Kubernetes API server, in the PEM format.
-
Service account token: A JWT (JSON Web Token) that authenticates the DoiT Console to access your Kubernetes cluster.
-
-
To test the connection to the cluster, select Test Connection. The Host, Cluster CA certificate, and Service account token fields must be correct for the test to pass.
-
Select Save.
Your cluster should now appear in the list of Assets with a Self-Managed type. You can now onboard this cluster by following the instructions below.
DoiT can track costs only for self-managed clusters that are hosted on AWS EC2 instances. To enable cost tracking, tag your EC2 instances with a user-defined allocation tag in this format: eks:cluster-name. See Enable cost tracking for clusters hosted on AWS EC2 for more details.
Onboard clusters
Kubernetes Intelligence relies on the Kubernetes Intelligence agent (PerfectScale Exporter) to collect cluster metrics. To onboard a Kubernetes cluster, you need to have the agent installed on the cluster.
-
In the DoiT console, select Integrate from the top navigation bar, and then select Assets.
-
Select Kubernetes from the left-hand menu. Here you'll find all the clusters uncovered via the daily scan by the DoiT platform. Self-managed clusters will not appear in the list until you add them separately as instructed in Connect self-managed clusters.
-
If you've onboarded clusters with PerfectScale, proceed to Option 1: Map clusters. Otherwise, go to Option 2: Install agent via Helm chart.
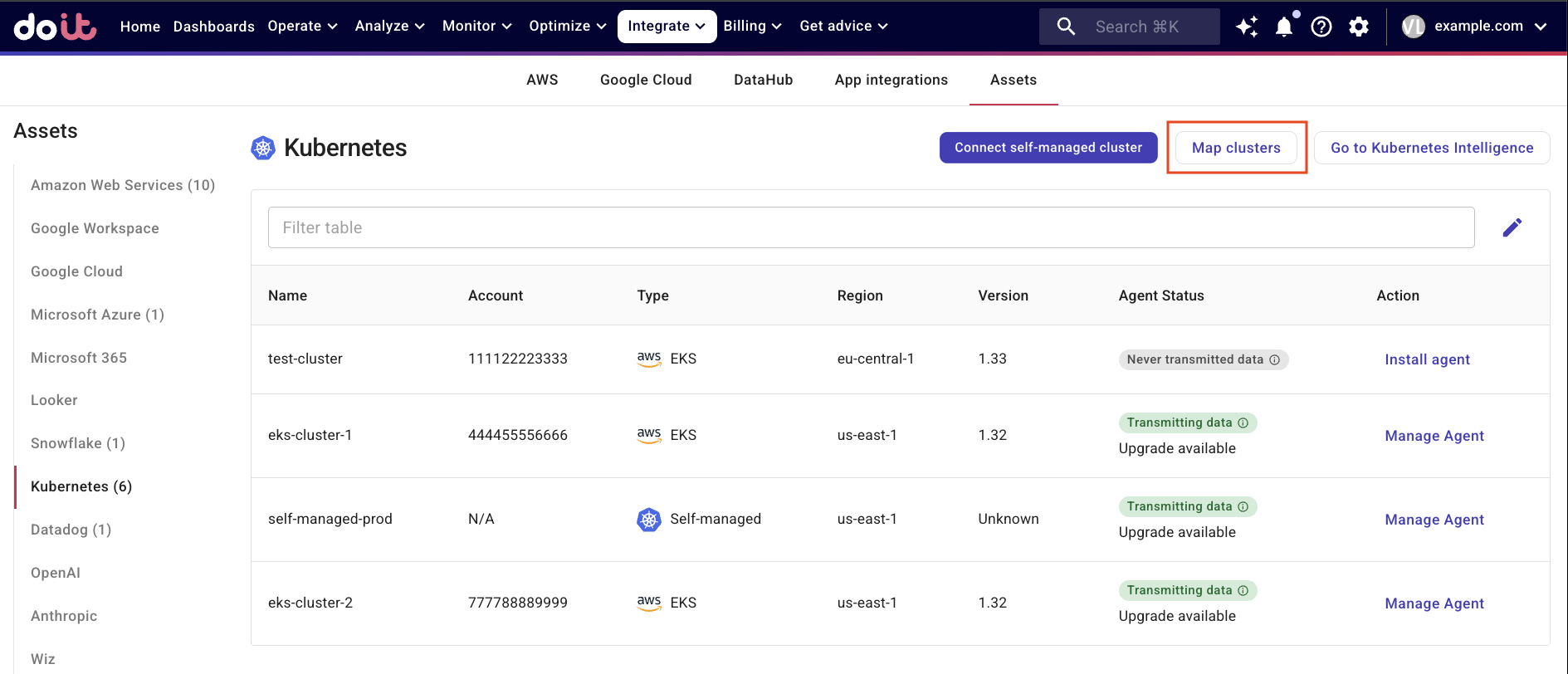
Option 1: Map clusters
This option lets you avoid reinstalling the agent on clusters that already onboarded PerfectScale.
Select Map clusters to specify mappings between PerfectScale clusters and their corresponding DoiT entities.

Option 2: Install agent via Helm chart
-
Install Helm on your local system if you haven't done so.
-
Make sure the
kubectlcommand-line tool is configured to communicate with your clusterThere are multiple ways to point
kubectlto the correct cluster. The instructions below are for reference purposes.- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- Google Kubernetes Engine
-
Associate your IAM user with the AmazonEKSClusterAdminPolicy access policy for the target cluster.
-
Create a
kubeconfigfile to connectkubectlto the EKS cluster, using the following command in the AWS CLI:aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <eks_cluster_name> --region <region>
-
Set your project property by running the
gcloud config set project <projectID>command. -
Update the
kubeconfigfile to pointkubectlat the GKE cluster, using the following command:gcloud container clusters get-credentials <gkeClusterName> --zone <zone> --project <projectID>
-
In the DoiT console, navigate to the Kubernetes assets list, locate the cluster of interest, and then select Install agent in the Action column.
If the DoiT platform identifies clusters that have installed the agent on PerfectScale but not mapped yet, you'll have the option to map the cluster and skip the following steps.
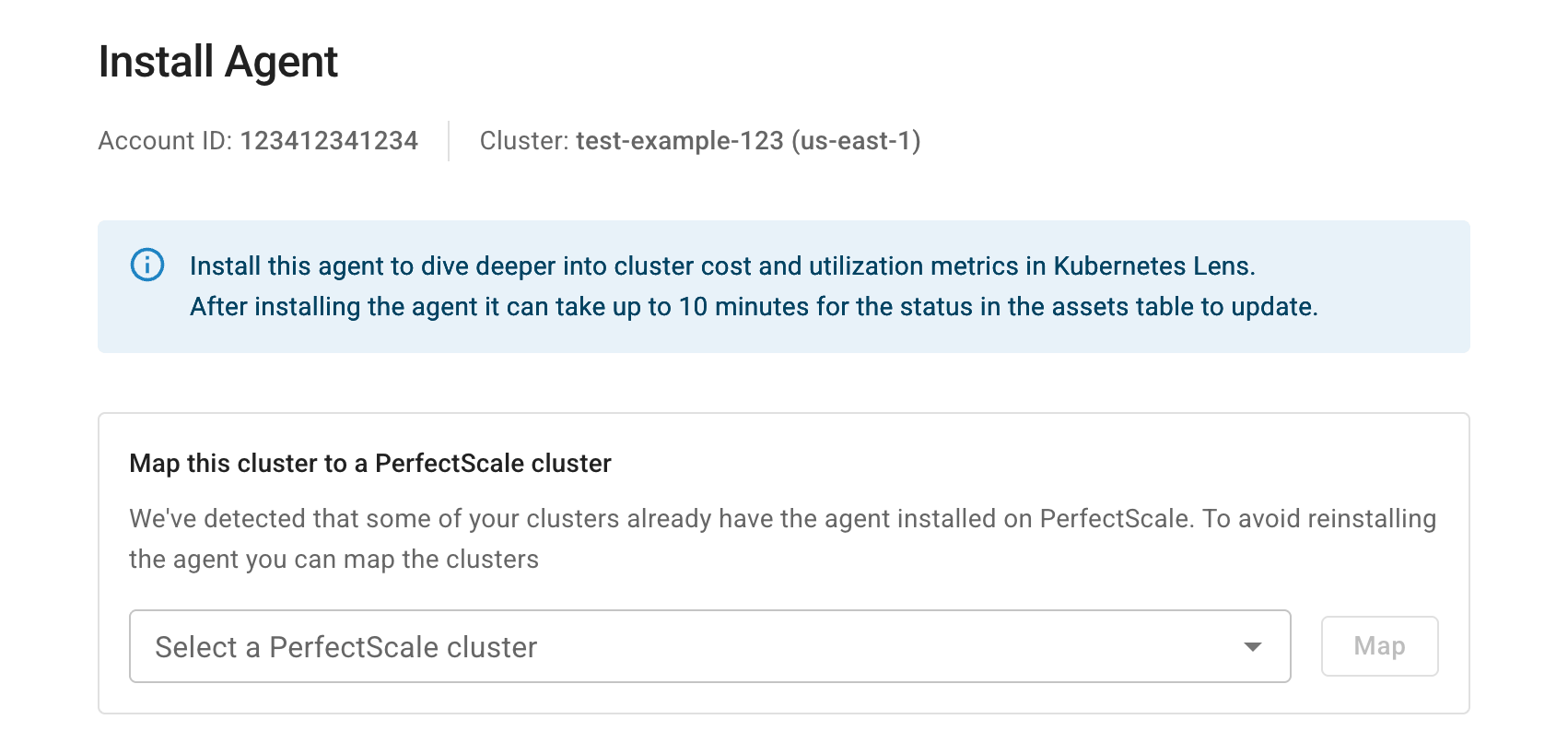
-
Copy and run the Helm command shown in the DoiT console to add the PerfectScale Helm chart repo.

-
Select Generate secret.
-
Note down the values of
secret.clientIdandsecret.clientSecretin the Helm command displayed on the DoiT console. -
Copy and run the Helm command to deploy the chart.
-
-
Select Done when the Helm deployment is completed.
Verify agent status
If the installation or mapping is successful, the Agent status of the cluster on the assets list will show Waiting for data. This status may last three minutes. After that, the status changes to Transmitting Data.
To onboard multiple clusters, repeat the steps above for each one.
It can take up to three minutes for the status in the assets table to update, and up to 24 hours before the data is available in the Kubernetes Intelligence.
(Optional) Enable cost tracking for clusters hosted on AWS EC2
To track costs for self-managed clusters hosted on AWS EC2 instances, you need to manually tag your EC2 instances with a user-defined cost allocation tag, such as eks:cluster-name. Make sure these tags are activated as cost allocation tags in your AWS billing. See Activating user-defined cost allocation tags and AWS cost allocation tags in DoiT platform.
DoiT scans the billing data on a daily basis. If your clusters are newly created (within 72 hours) or have no spend, DoiT will not detect them.
Offboard clusters
To offboard a cluster, run the following kubectl command. Deleting the namespace removes the agent from the cluster and stops all data transmission.
kubectl delete namespace perfectscale
You can also find the command in the instructions to Delete agent.
▶️ Interactive demo
Try out our interactive demo for a hands-on walk-through experience.
If the demo doesn't display properly, expand your browser window or open the demo in a new tab.