Work with Databricks data
Once you've imported your Databricks data into the DoiT platform, you can start analyzing and monitoring your Databricks cost and usage. Databricks data is tracked and reported on an hourly basis.
Databricks system tables
The DoiT console interacts with the following Databricks system tables:
| System Table | Description |
|---|---|
system.billing.usage | Includes records for all billable usage across your account. |
system.billing.list_prices | A historical log of SKU pricing. A record gets added each time there is a change to a SKU price. |
system.compute.node_timeline | Captures the utilization metrics of your all-purpose and jobs compute resources. |
system.access.workspaces_latest | Contains metadata for all the workspaces in the account. |
system.compute.clusters | Contains the full history of compute configurations over time for any cluster. |
system.compute.warehouses | Contains the full history of configurations over time for any SQL warehouse. |
The required permissions are granted when you create a service principal for the DoiT connector.
Databricks data in Cloud Analytics
You can get Databricks data through dimensions and metrics. See below for the mapping between the DoiT and Databricks terminologies.
Basic metrics
DoiT term | Databricks term | Description |
|---|---|---|
cost | cost | The total cost for Databricks Units (DBUs) consumed by compute workloads (such as clusters, SQL warehouses) and the separate charges from your chosen cloud provider for the underlying infrastructure. |
usage | usage | The consumption of Databricks compute resources (DBUs) and specific features used by workloads and users. |
Standard dimensions
| DoiT term | Description |
|---|---|
| Billing Account | The unique identifier of the specific Databricks account. Maps to the account_id in the billing usage table schema. |
| Project ID | The unique identifier of the Databricks warehouse. Maps to the workspace_id in the billing usage table schema. |
| Project/Account name | The name of the Databricks workspace. Maps to the workspace_name in the workspaces system table schema. |
| Usage start time | The start of the hour or billing interval during which the recorded usage occurred. Maps to the usage_start_time in the billing usage table schema. |
| Usage end time | The end of the billing interval during which the recorded usage occurred. Maps to the usage_end_time in the billing usage table schema. |
| Service ID/description | The specific Databricks product or feature that was the ultimate source of the billable usage. Maps to the billing_origin_product in the billing usage table schema. For example, SQL, ALL_PURPOSE, or INTERACTIVE. |
| SKU ID/Description | The specific Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) that was consumed and incurred costs for a particular usage record. Maps to the usage_sku_name in the billing usage table schema. For example, STANDARD_ALL_PURPOSE_COMPUTE, SQL_CLASSIC_COMPUTE, or ENTERPRISE_ALL_PURPOSE_COMPUTE_(PHOTON). |
| Report cost | The estimated cost in dollars (or your configured currency) for a specific unit of usage. Maps to the usage_quantity in the billing usage table schema and pricing in the pricing table schema. |
| Report usage | The number of units that a particular Databricks product, feature, or resource consumed during the recorded time interval. The usage_quantity depends on the usage_unit. For example, if the usage_unit is STORAGE_SPACE, then usage_quantity might be in TB-hours or GB-hours. Maps to the usage_quantity in the billing usage table schema. |
| Usage unit | The unit of measurement for usage_quantity. Maps to the usage_unit in the billing usage table schema.For example, DBU, STORAGE_SPACE, NETWORK_BYTE, or API_OPERATION. |
| Cost type | Whether the usage record is an original entry or if its related to a correction made by Databricks. Maps to the record_type in the billing usage table schema. For example, ORIGINAL, RETRACTION, or RESTATEMENT. |
| Resource ID | The unique identifier assigned to various objects or entities with Databricks that consume or manage compute, storage, or data. |
| Operation | A Databricks action or task performed with the platform that consumes compute resources and incurs charges measured in DBUs. |
| Row ID | The unique identifier for each individual usage record (row) in the table. Maps to the record_id in the billing usage table schema. |
System labels
Below are the Databricks system labels that you can use in the DoiT platform.
-
databricks/account_id: The unique identifier of the specific Databricks account.
-
databricks/cloud: The cloud provider the Databricks warehouse is using. For example,
AWS,AZURE, andGCP. -
databricks/cluster_name: The Databricks cluster name.
-
databricks/usage_type: The workload type or specific feature that is consuming DBUs. For example,
STORAGE_SPACE. -
databricks/warehouse_name: The Databricks warehouse name.
Identity metadata
identity_metadata provides more information about the identities involved in the usage.
-
databricks/identity_metadata/run_as: Logs who ran the workload. These values are only populated for certain workload types listed in Identity metadata reference.
-
databricks/identity_metadata/owned_by: This only applies to SQL warehouse usage and logs the user or service principal who owns the SQL warehouse responsible for the usage.
-
databricks/identity_metadata/created_by: This applies to Databricks Apps and logs the email of the user who created the app.
Usage metadata
The values in usage_metadata are strings related to the workspace objects and resources involved in the usage record. See Usage metadata reference.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/cluster_id: The unique identifier of a compute cluster instance.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/destination_region: The AWS or Azure region where data is being transferred to or where a resource is being replicated.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/notebook_id: The unique identifier of the notebook associated with the Databricks usage.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/dlt_pipeline_id: The unique identifier of the declarative pipeline associated with the usage record
-
databricks/usage_metadata/dlt_update_id: The unique identifier of the pipeline update associated with the usage record.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/dlt_maintenance_id: The unique identifier of the pipeline maintenance tasks associated with the usage record.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/run_name: The unique user-facing name of the Foundation Model Fine-tuning run associated with the usage record.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/notebook_path: The workspace storage path of the notebook associated with the usage.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/central_clean_room_id: The unique identifier of the central clean room associated with the usage record.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/app_id: The unique identifier of the app associated with the usage record.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/budget_policy_id: The unique identifier of the serverless budget policy attached to the workload.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/endpoint_id: The unique identifier of an API endpoint.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/endpoint_name: The name given to an endpoint, such as Model Serving endpoint.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/job_id: The unique identifier assigned to a Databricks job.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/job_name: The user-supplied, human-readable name given to a Databricks job.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/job_run_id: The unique identifier assigned to a specific execution of a Databricks job.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/metastore_id: The unique identifier of a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/node_type: The specific type of virtual machine (VM) instance used for a cluster node in Databricks.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/source_region: The AWS or Azure region where data is originating from or where a resource is intially located.
-
databricks/usage_metadata/warehouse_id: The unique identifier of a Databricks SQL warehouse.
Product features reference
product_features is an object containing information about the specific product features used and includes the following key/value pairs:
-
databricks/product_features/jobs_tier: Values include
LIGHT,CLASSIC, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/sql_tier: Values include
LIGHT,CLASSIC, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/dlt_tier: Values include
CORE,PRO,ADVANCED, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/is_serverless: Values include
trueorfalse, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/is_photon: Values include
trueorfalse, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/serving_type: Values include
MODEL,GPU_MODEL,FOUNDATION_MODEL,FEATURE, ornull. -
databricks/product_features/offering_type: Values include
BATCH_INFERENCEornull. -
databricks/product_features/networking_connectivity_type: Values include
PUBLIC_IPandPRIVATE_IP.
Extended metrics
DoiT supports Databricks Cluster CPU utilization and Cluster memory utilization metrics. These appear under Extended metrics.
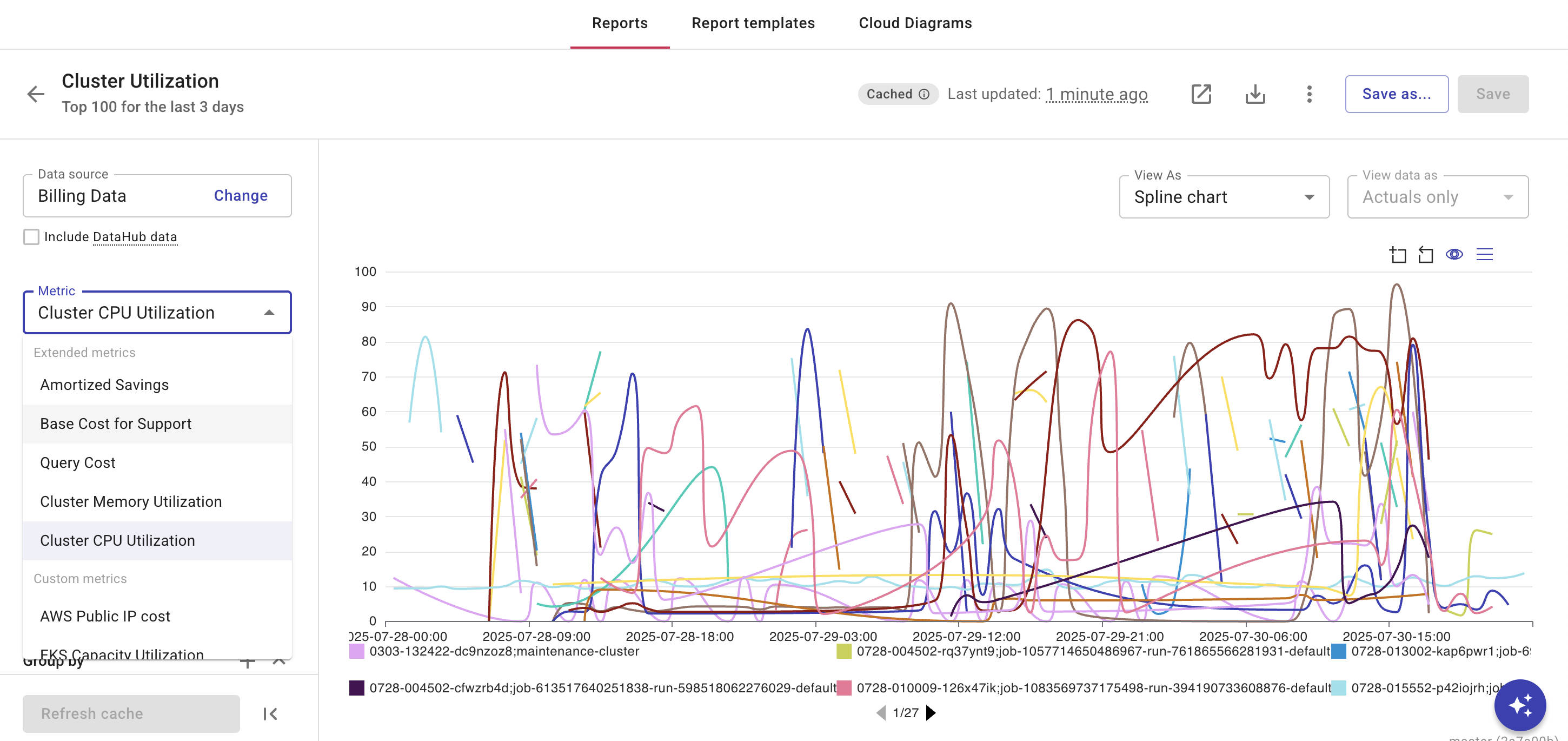
These metrics provide the operational context needed to translate DBU costs into actionable insights. For example, if a cluster consistently shows high CPU or memory utilization, it indicates a bottleneck, meaning your cluster may be under-provisioned for its workload. You might need to add more nodes or optimize your code.
Cluster CPU utilization
Cluster CPU utilization measures the percentage of time your cluster's CPUs are actively processing tasks. It's broken down into user mode (your workload), system mode (kernel operations), and idle time.
Cluster memory utilization
Cluster memory utilization measures the percentage of RAM being used on your cluster's nodes. It tracks memory allocated to Spark executors, cached data, and system processes, distinguishing between used, free buffer, and cached memory.