PerfectScale for Spot FAQ
Spot Instance
What is a Spot Instance?
Spot Instances are spare EC2 capacity that can save you up to 90% off On-Demand prices that Amazon Web Services can interrupt with a two-minute notification. Spot uses the same underlying EC2 instances as On-Demand and Reserved Instances and is best suited for fault-tolerant, flexible workloads. Spot instances provide an additional option for obtaining compute capacity and can be used along with On-Demand and Reserved Instances.
What are the differences between Spot Instances and On-Demand Instances?
While running, Spot Instances are essentially the same as On-Demand Instances. The main difference is that Spot Instances typically offer a significant discount over On-Demand prices. The tradeoff is that Spot Instances can be interrupted by Amazon EC2 for capacity requirements with a two-minute notification. Spot prices adjust gradually based on long-term supply and demand for spare EC2 capacity. See Amazon EC2 Spot Instances for more information.
When to use Spot Instances?
Spot Instances are most suitable for applications that have fault tolerance built-in, are stateless, or perform data processing in large clusters (for example, Hadoop).
Additional use cases include:
- Batch processing — you can use the AWS Batch service in combination with Spot Instances to run batch processing on Spot Instances that are currently available at a low cost. This can generate significant cost savings compared to running the same batch process using On-Demand Instances.
- Continuous integration — development and testing are common in a cloud environment. Dev/test tasks typically run on an irregular schedule, and because they are not production workloads, they can tolerate occasional interruptions.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) — you can use Spot Instances to run massively parallel workloads like artificial intelligence analytics applications. These applications run on graphical processing units (GPUs), and since GPU instances are expensive, Spot Instances can be a big help.
What are the best practices to use Spot Instances?
We recommend using more than one Availability Zone and being flexible about the instance types to maximize the amount of Spot capacity available to you. A Spot capacity pool is a set of unused EC2 instances with the same instance type, operating system, Availability Zone, and network platform (EC2-Classic or EC2-VPC).
What price will I pay for a Spot Instance?
With Spot Instances, you pay the Spot price that's in effect for the time your instances are running. Spot Instance prices are set by Amazon EC2 and adjust gradually based on long-term trends in supply and demand for Spot Instance capacity. For more information, refer to the AWS Spot Instance advisor.
What if there are no available Spot Instances?
PerfectScale for Spot supports fallback to On-Demand for scenarios where there are no available Spot Instances to ensure your workload availability, and it reverts to Spot Instances as soon as they are available again.
PerfectScale for Spot
How does PerfectScale for Spot calculate the potential savings?
The potential savings are calculated based on the following:
- The number of the desired instances in the Auto Scaling Group
- The difference between On-Demand prices and Spot prices per hour
- The number of hours in a given month (approximately 730 hours)
What is the proportion of the Spot and On-Demand Instances?
By default, PerfectScale for Spot recommends that 20% of desired capacity exists On-Demand and 80% with Spot Instances. You can change the percentage of On-Demand Instances and Spot Instances via the DoiT console or the instance distributions tags.
Can I change the allowed instances type list?
You can exclude instance types that aren't fulfilling your workload requirements in the DoiT console. See Modify Recommendations.
What AWS technologies does PerfectScale for Spot work with?
PerfectScale for Spot works with any AWS technology that uses Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs) to function.
Does PerfectScale for Spot support Amazon Elastic Beanstalk?
Yes. AWS Elastic Beanstalk uses an ASG to manage your Amazon EC2 instances.
Does PerfectScale for Spot support Amazon ECS?
PerfectScale for Spot supports the AWS Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) with the EC2 launch type, which, in turn, uses ASGs to function (see above).
However, PerfectScale for Spot does not support Amazon ECS with the Fargate launch type, because AWS Fargate does not use ASGs.
Does PerfectScale for Spot support Amazon EKS?
Yes. Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) supports the Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler, which, in turn, uses ASGs to function (see above).
The Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler is a core component of a Kubernetes control plane that automatically adjusts the number of nodes in your cluster when pods fail or are rescheduled onto other nodes. Applying PerfectScale for Spot recommendations to your EKS environment allows you to generate savings by running Spot Instances.
You can use the AWS Node Termination Handler, an open-source project maintained by Amazon, to ensure "that the Kubernetes control plane responds appropriately to events that can cause your EC2 instance to become unavailable, such as EC2 maintenance events, EC2 Spot interruptions, ASG Scale-In, ASG AZ Rebalance, and EC2 Instance Termination via the API or Console."
Does PerfectScale for Spot support Amazon EMR?
No. PerfectScale for Spot doesn't support Amazon EMR because it doesn't use ASGs. AWS EMR uses its own type of autoscaling, called managed scaling.
PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment
What is PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment?
DevOps and Platform teams often prefer using infrastructure as code (IaC) tools to implement cloud infrastructure. IaC tools allow them to replace manual work required for IT resource management and provisioning cloud resources with simple lines of code. Auto-Enrollment is the feature that meets this need by leveraging AWS ASG Tags.
See AWS tags: PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment for more information.
What does it mean that PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment is tool-agnostic?
With IaC, configuration files are created containing the infrastructure specifications, making it easy to edit and distribute configurations. There are a variety of IaC tools available, for example, Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Azure Resource Manager, and GCP Cloud Deployment Manager.
PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment is tool-agnostic in the sense that the tags you need (doitintl:spotscaling:auto-enroll and doitintl:fallback-to-on-demand) are independent of the IaC tool you use.
What is the default behavior of PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment?
PerfectScale for Spot Auto-Enrollment behaves the same as when you apply the recommendations in the DoiT console. By default, PerfectScale for Spot recommends that 20% of desired capacity exists On-Demand and 80% with Spot Instances. The same for the allowed instance type, PerfectScale for Spot recommends similar machine types based on vCPUs and memory configuration.
Error messages
Incompatible launch template: already requesting for spot instances
This error happens when PerfectScale for Spot tries to create a mixed instances group using a launch template that already requests Spot Instances.
To solve the issue, you need to create a new launch template or a new version of the same template without specifying the Purchasing option of Request Spot Instances in the Advanced Details section.
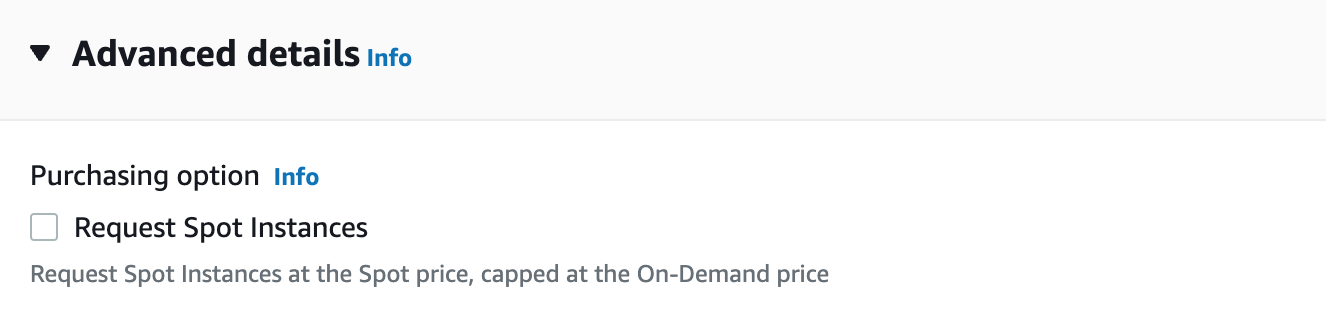
A launch template lets you configure additional settings in your Auto Scaling group to launch multiple instance types and combine On-Demand and Spot purchase options. To launch instances with such a combination, you must not specify the Spot Instance request in the launch template (see Limitations). Otherwise, you would see the following error message on the DoiT console ASGs screen:
Incompatible launch template: already requesting for spot instances
The error message from AWS is:
Incompatible launch template: You cannot use a launch template that is set to request Spot Instances (
InstanceMarketOptions) when you configure an Auto Scaling group with a mixed instances policy. Add a different launch template to the group and try again.
Incompatible launch template: launch configuration is not supported
If you're using launch configurations, you won't be able to benefit from the PerfectScale for Spot capabilities.
Since December 31, 2022, AWS doesn't support launch configurations, so you should be using launch templates instead. To learn how to migrate to launch templates, see AWS documentation.
Incompatible launch template: this launch template has specific settings in storage, network interfaces, or advanced details
At the moment, we don't support launch templates with specific settings in storage, network interfaces, or advanced details. In order to use PerfectScale for Spot, you need to create a version of the launch template you wanted to use, but without these additional settings.